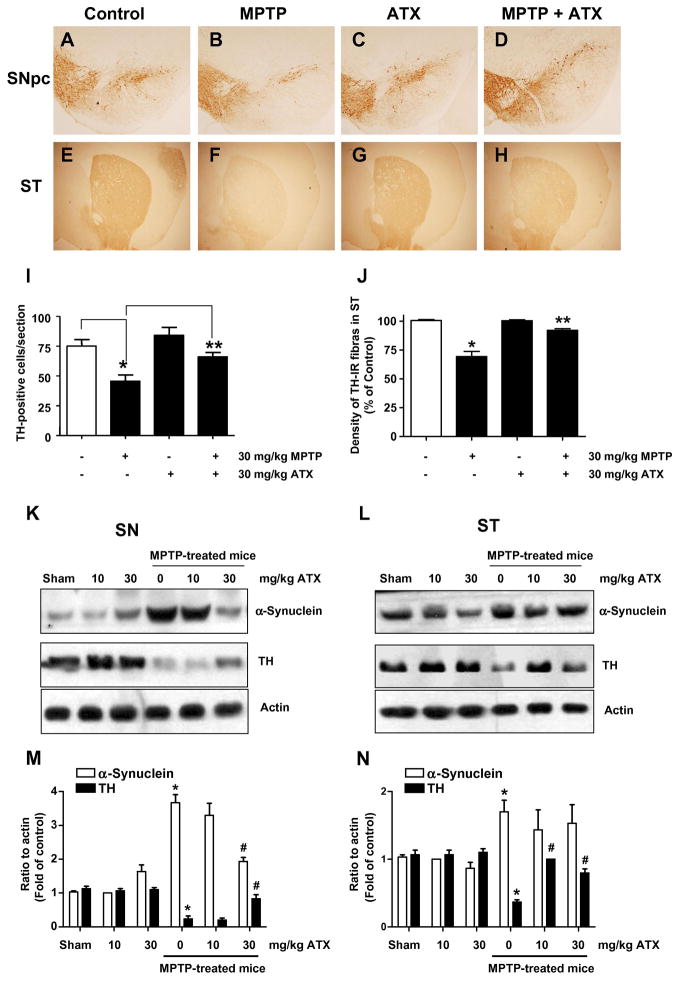
Fig. 6.
Effects of AST on nigra TH expression and dopaminergic neurons in the mouse MPTP model. (A) Immunohistochemical staining of dopaminergic neurons with an anti-TH antibody in the substantia nigra (SN). Photomicrographs were taken at a magnification of 200×. a, control group. b, MPTP-treated group (30 mg/kg, 1×/day for 28 days). c, AST-treated group (30 mg/kg), d, MPTP + AST-treated group. (B) The immunoreactive cell counts in the SN pars compacta of control group, MPTP-treated group, AST-treated group, and AST + MPTP group. Values represent means ± S.E.M of 4 mice per group. *p <0.05 compared with the control group; and **p <0.01 compared with the MPTP-treated group. (C) and (D) TH and α-synuclein expression was determined in the SN (C) and stria terminalis (ST) (D). Lysates containing equal amounts of protein (20 μg) from SN or ST tissue samples were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotted with anti-α-synuclein or anti-TH antibody. Actin was shown as an internal standard.