Figure 3.
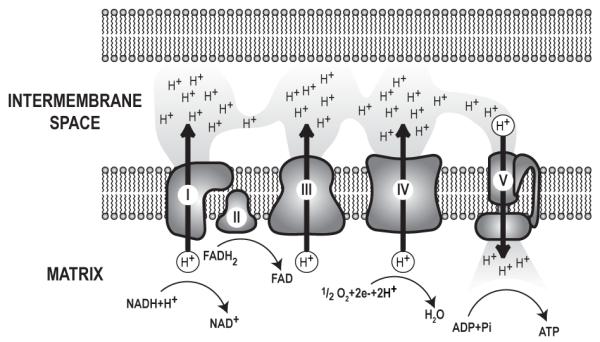
The electron transport chain: Electron transport chain complexes I-V are part of the inner mitochondrial membrane. NADH and FADH2 from the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle donate electrons to complexes I and II, respectively. These electrons are transferred to complex III and complex IV, sequentially. With each transfer, the electrons release energy. Energy release from electrons is coupled to the movement of protons from the matrix to the intermembrane space, resulting in a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Upon reaching complex IV, electron pairs combine with ½ O2 and 2H+ to create H2O. Complex V, or ATP synthase, releases energy stored in the proton gradient by allowing proton flow into the matrix. Complex V couples this energy release to the synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi. Each complex is assembled from a number of proteins. For example, complex I, the largest complex, has 39 proteins encoded in the nuclear DNA and 7 proteins encoded in the mtDNA, while complex II, the smallest complex, has 4 nuclear encoded proteins.
