Fig. 2.
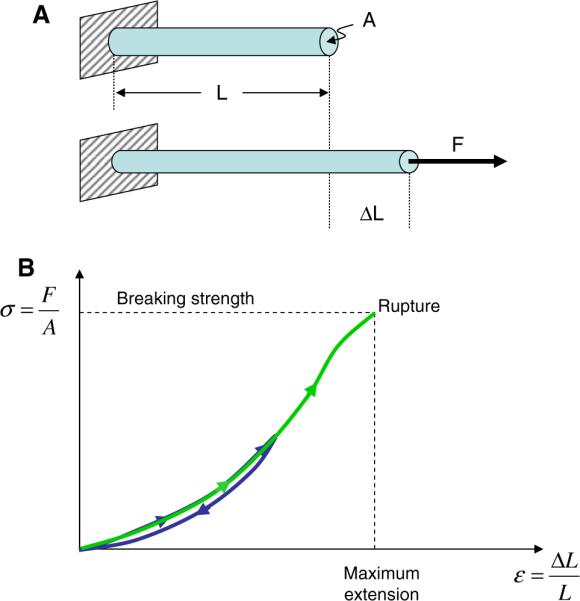
Stress–strain curves of stretched fibers. (A) A force F is applied in the longitudinal direction to a fiber with length L and cross sectional area A. The fiber extends by an amount ΔL. (B) A schematic stress–strain curve of the stretching of a fiber. The slope of the curve corresponds to the stiffness of the fiber. In a linear, elastic model, the stiffness (slope) is the called Young's modulus of the material. The maximum extension at which the fiber ruptures is called breaking strain (or extensibility) of the fiber
