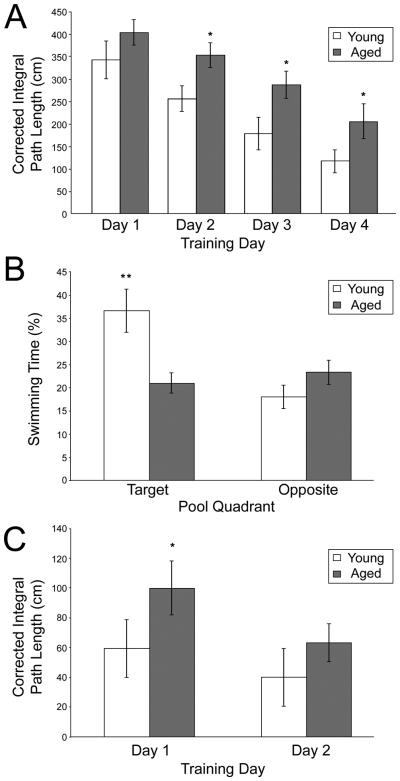
Figure 1.
Aged rats are impaired in the Morris swim task. Young adult rats swam a significantly shorter paths to reach the hidden platform than did the aged rats (A), and this difference was significant on days 2, 3 and 4 of training. During the probe trial (B), young adult rats spent significantly more time in the target quadrant, but not the opposite quadrant, compared to aged rats. During visible platform trials (C), young adult rats took significantly shorter paths to the visible platform than did aged rats on day 1, but this difference was no longer apparent by day 2 of training (all data are mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, young vs. aged animals).