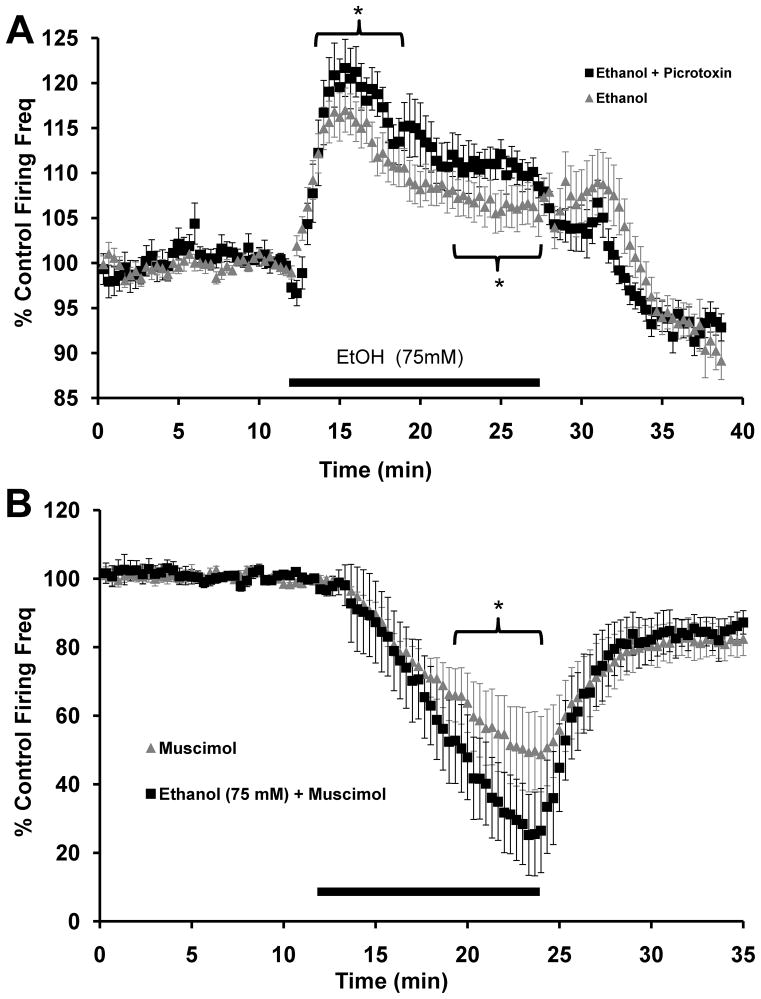
FIGURE 4. Ethanol modulation of VTA-DA activity is regulated by GABAA receptors.
A. Cumulative graph displaying average firing rate of VTA-DA neurons treated with ethanol (75 mM; n = 30; reproduced from Fig. 1) and ethanol (75 mM) in the continued presence of picrotoxin (75 μM; n = 14). The average baseline firing rate for ethanol with picrotoxin was 1.9 ± 0.1 Hz (* indicates p<0.01 by one-way ANOVA). B. Cumulative graph displaying average firing rate of VTA-DA neurons treated with muscimol (1 μM; n = 8; reproduced from Fig. 2B) and ethanol (75 mM) with muscimol (n = 9). The average baseline firing rate for ethanol with muscimol was 2.6 ± 0.6 Hz (* indicates p<0.01 by one-way ANOVA). For both A and B, data points for individual cells represent 20-sec sweeps in which the average firing rate (Hz) was calculated. Each data point is normalized to the last 5 mins of baseline. The normalized data points were combined to obtain the graphs above. Error bars represent the SEM of averaged time points. Note differences in scale.