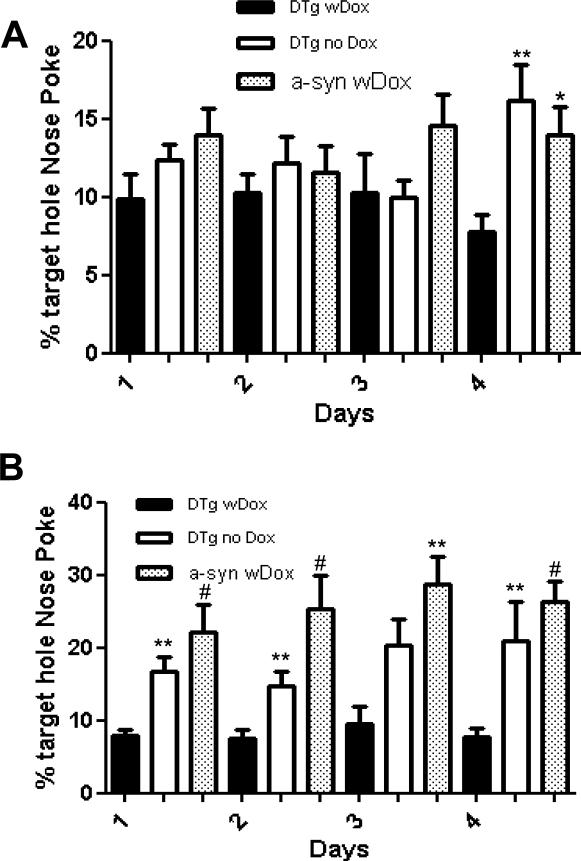
Fig 2.
Nose poke odor detection/identification test at 8 months (A) and at 12 months of age (B) over a 4 day repeat trial period. The percentage of nose pokes in the target versus other holes was calculated and reported as mean ± SEM. 6.25% represents a random nose-poke (1/16 chance). DTg + Dox (black filled bar) as compared to DTg - Dox and a-syn + Dox. (*: p<0.05, **: p<0.01, and #: p<0.001, Mann-Whitney U test).