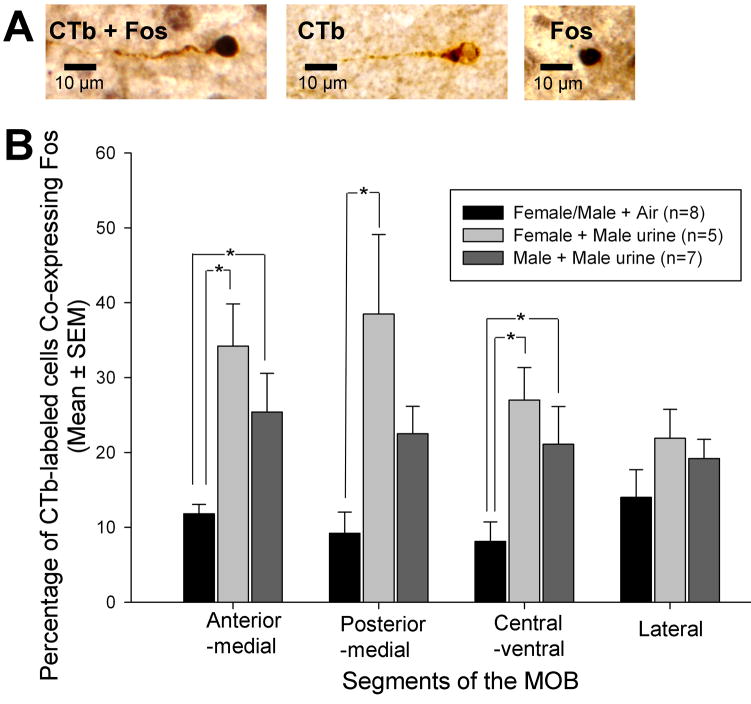
Figure 4.
Effect of volatile male urinary odor exposure on the co-expression of Fos in MOB M/T cells of female and male mice that were retrogradely labeled by a prior injection of cholera toxin B (CTb) into the medial amygdala (Me). Panel A: Three possible types of labeling occurred in MOB M/T cells following Me CTb injections and urinary odor exposure: CTb/Fos double-labeled (CTb + Fos), CTb-single labeled (CTb), and Fos-single labeled (Fos) M/T cells. Panel B: The percentage of CTb-labeled (Me-projecting) M/T cells that co-expressed Fos across 4 segments of the MOB following exposure to volatile male urinary odors or to clean air. Note that male and female subjects exposed to clean air were combined into a single control group. * P<0.05, Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc comparisons between pairs of treatment groups following a significant overall ANOVA.