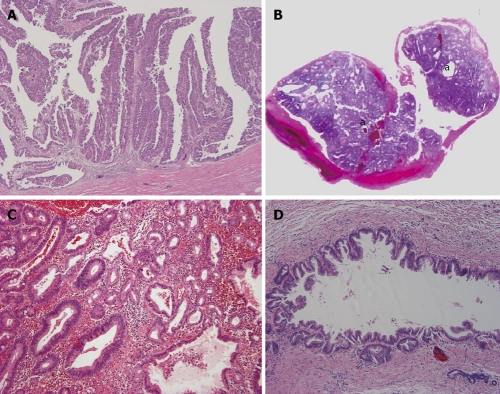
Figure 4.
Intraductal type of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. A: Intraductal papillary neoplasm of bile duct. Neoplastic biliary epithelia show papillary growth in the dilated lumen. There is no invasion into the duct wall; B: Intraductal tubular neoplasm of bile duct. The neoplasm (a) appears as a cast in the dilated lumen; C: Intraductal tubular neoplasm of bile duct. The tubular pattern is predominant. Higher magnification of Figure 4B; D: Superficial spreading type. Carcinoma cells show intraductal, intraepithelial growth with a micropapillary configuration and intraglandular involvement. There is no evident invasion into the duct wall.