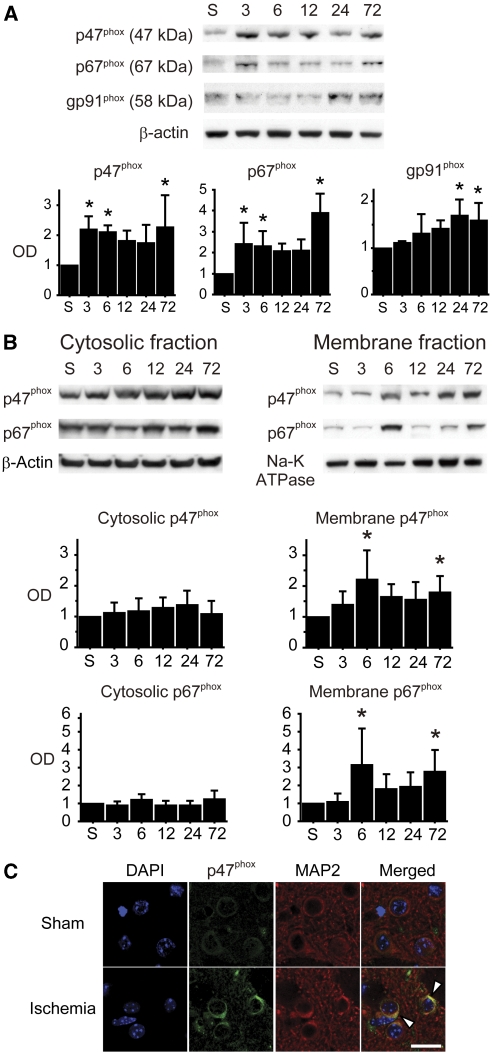
Figure 2.
Upregulation and activation of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase (NOX) after transient global cerebral ischemia (tGCI). (A) Western blots using whole cell lysate samples show biphasic upregulation of the cytosolic subunits (p47phox and p67phox) at the early (3 to 6 hours) and late (72 hours) phases after tGCI. In contrast, the membrane-bound subunit gp91phox upregulated 24 and 72 hours after tGCI (n=4, *P<0.05 compared with sham). S, sham; OD, optical density. (B) Western blot analysis showed increase of cytosolic subunits (p47phox and p67phox) in the membrane fraction 6 and 72 hours after ischemia (n=5, *P<0.05 compared with sham). In the cytosolic fraction, no significant differences were seen at any time point. β-Actin and Na-K ATPase were used as internal controls for the cytosolic and membrane fractions, respectively. (C) Representative confocal images of immunostaining. Expression of p47phox became more intense, especially on the cell surface (arrowheads), 6 hours after ischemia. Microtubule-associated protein-2 (MAP2) immunostaining demarcates the neuronal cytoplasmic space. Nuclei were counterstained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Scale bar=20 μm.