Figure 8.
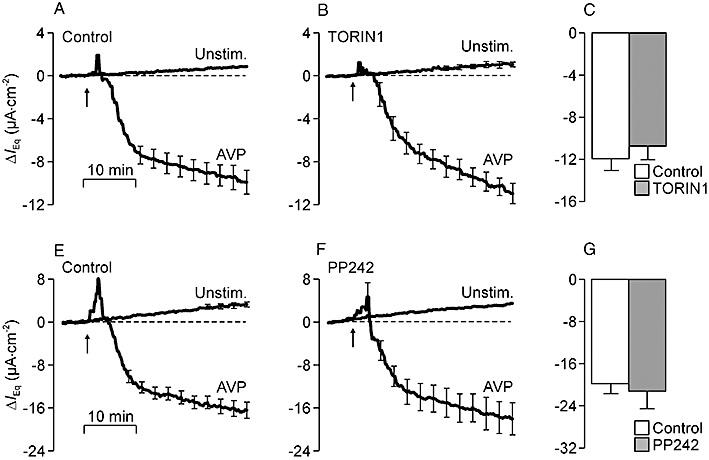
Effects of TORIN1 and PP242 upon the electrometric response to arginine vasopressin (AVP). (A) Changes in equivalent short circuit current (IEq) (n = 4) measured in studies of unstimulated (Unstim.) and AVP-stimulated (10 nM, basolateral, arrows) control cells (basal IEq unstimulated cells: −15.8 ± 0.6 µA·cm−2; basal IEq AVP-stimulated cells: −13.1 ± 1.0 µA·cm−2). (B) Data from age-matched cells that were pretreated (30 min) with 100 nM TORIN1 (basal IEq unstimulated cells: −12.8 ± 1.5 µA·cm−2; basal IEq AVP-stimulated cells: −13.3 ± 2.0 µA·cm−2). (C) Responses to AVP in control and TORIN1-treated cells were quantified by measuring the change in IEq that developed during exposure to AVP and subtracting the spontaneous change measured in unstimulated cells. (E) Data (n = 5) from separate control experiments showing the spontaneous and AVP-induced changes in IEq (basal IEq unstimulated cells: −27.5 ± 2.8 µA·cm−2; basal IEq AVP-stimulated cells: −30.3 ± 1.4 µA·cm−2). (F) Data from age-matched cells at identical passage that had been pretreated (30 min) with 1 µM PP242 (basal IEq unstimulated cells: −20.8 ± 1.8 µA·cm−2; basal IEq AVP-stimulated cells: −22.4 ± 1.6 µA·cm−2). (G) Responses to AVP quantified in control and PP242-treated cells.
