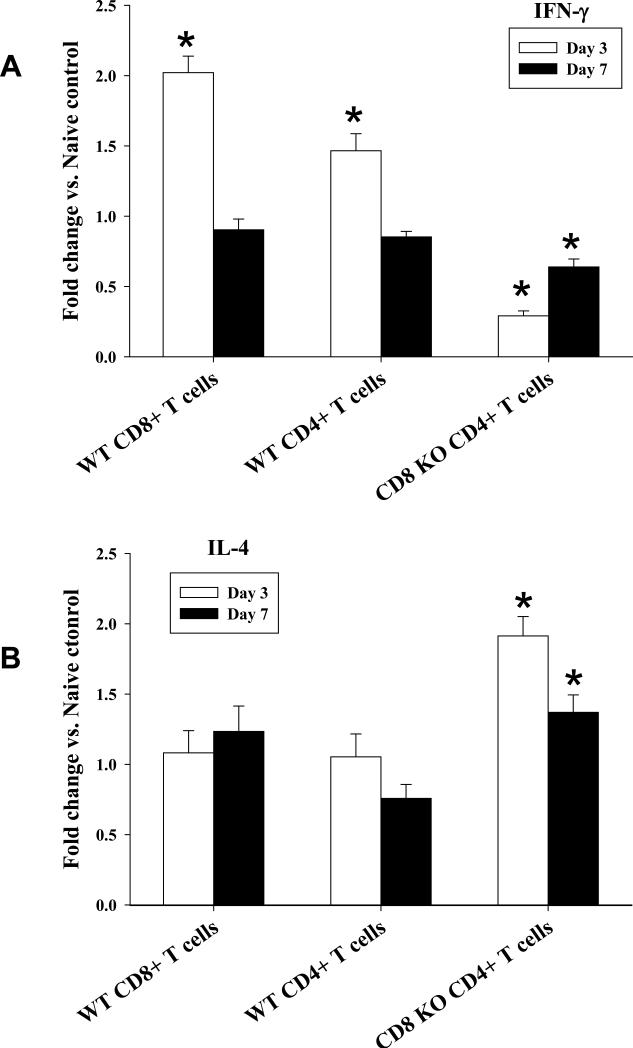
Figure 3. CD4+ T cells switch from an IFN-γ-dominant to an IL-4-dominant cytokine expression in the absence of CD8+ T cells.
Splenocytes were isolated from CD8 KO and wild-type recipient mice on day 3 and 7 post-transplant. Total RNA was then purified and cDNA for IFN-γ and IL-4 was amplified utilizing real-time PCR. CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were isolated and purified from splenocytes using negative selection columns A) IFN-γ mRNA derived from wild-type recipients was significantly upregulated in CD8+ T cells (2.0±0.1 fold, p<0.0001) and in CD4+ T cells (1.5±0.1 fold, p=0.0020). Conversely, CD4+ T cells from CD8 KO recipients demonstrated downregulation of IFN-γ (0.3±0.01 fold, p=0.0004). B) IL-4 mRNA was significantly upregulated in CD4+ T cells isolated from CD8 KO (1.9±0.1 fold; p=0.0005) but not in wild-type recipients. Data were expressed as the mean fold increase relative to cells collected form naïve control mice. All real-time PCR data were normalized to the level of mouse β-actin mRNA. Error bars denote the standard deviation of duplicate experiments (triplicate wells/sample). Significant upregulation or downregulation is denoted by “*”.