Fig. 5.
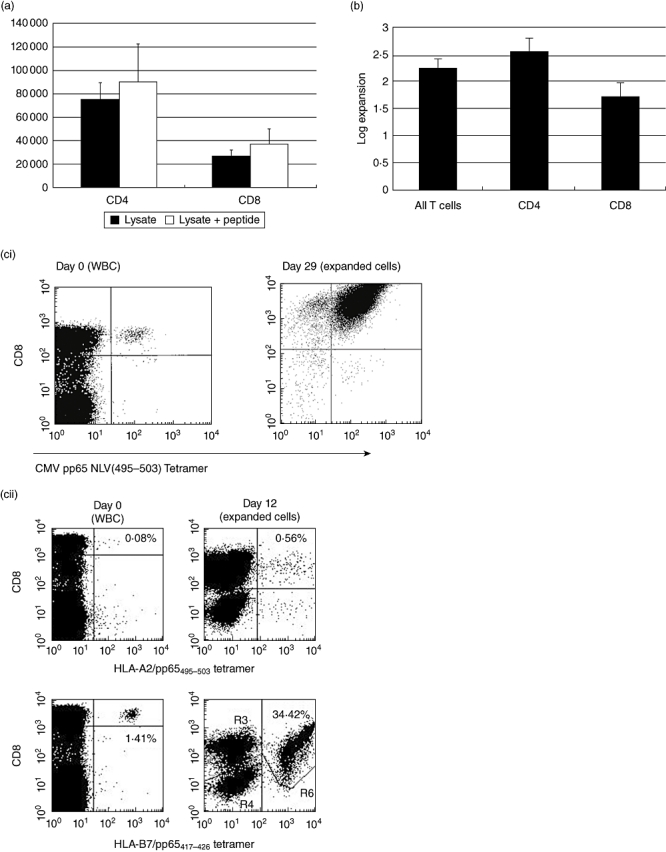
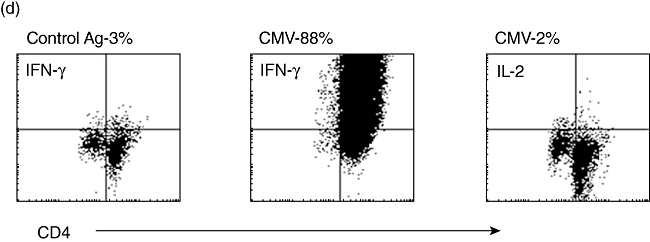
(a) Mean [±standard error of the mean (s.e.m.)] numbers of CD4 and CD8 T cells isolated using the interferon (IFN)-γ secretion assay per 108 starting human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) after stimulus with cytomegalovirus (CMV)-lysate for 16 h (n = 20). Addition of the human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-A2-specific NLV(495–503) peptide from pp65 increases the numbers of CD8+ cells isolated, with an apparent bystander effect on CD4+ cells (n = 8). (b) Mean (± s.e.m.) expansion rate of T cells isolated using the IFN-γ secretion assay and expanded as per Rauser et al. [9]. CD4+ cells show an advantage in expansion rates over CD8+ cells. (c) (i) HLA-A2+ human PBMC stimulated with the HLA-A2 restricted NLV(495–503) peptide from pp65 before isolation of positive cells using the IFN-γ secretion assay (day 0–0·04% of the start total of 108 PBMC – 40 000+ cells). The isolated and expanded cells after two rounds of expansion are >99% NLV(495–503) tetramer+ and have reached 108 cells in total (day 29). (ii) HLA-A2+ HLA-B7+ human PBMC stimulated with pp65 PepTivator peptide pool. Pre-stimulus B7-restricted CD8- T cells heavily outnumber A2-restricted cells (day 0). After stimulus, isolation using the IFN-γ secretion assay and one round of expansion (day 12) the very heavy bias towards the B7-restricted cells is maintained, with 34·42% of all cells B7-restricted. (d) CD4+ T cells stimulated with CMV lysate, isolated using the IFN-γ secretion assay, and expanded for 12 days post-isolation. Restimulated with autologous dendritic cells and CMV or control lysate and assayed for intracellular IL-2 or IFN-γ expression after 6 h. The vast majority make IFN-γ to CMV-restimulation but make no IL-2, confirming the effector-memory status of these helper cells.
