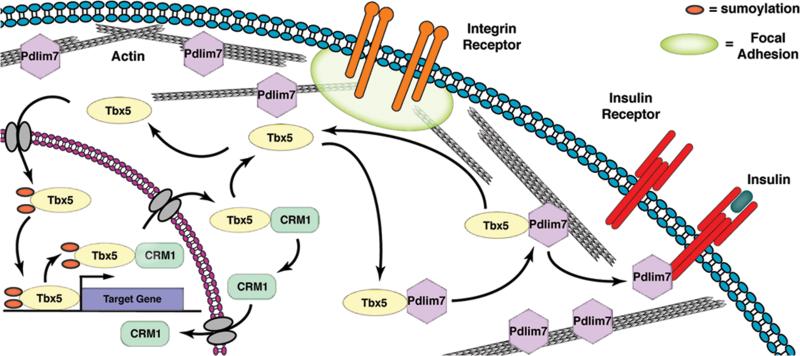
Figure 4.
Model for the diverse and multi-compartmental functions of PDZ-LIM proteins. PDZ-LIM proteins are engaged in dynamic interactions with cellular proteins. For example, Pdlim7 facilitates shuttling of Tbx5 between nucleus and actin cytoskeleton. Export of Tbx5 from the nucleus is promoted by CRM1, and protein subcellular localization and function possibly regulated by reversible sumoylation. Besides tethering Tbx5 to the actin cytoskeleton, Pdlim7 can interact with other cellular proteins, including the activated InsR. Pdlim7 uses the same domain to bind either Tbx5 or InsR and this competitive interaction may provide a mechanism for Tbx5 release from filamentous actin and relocation to the nucleus. Transmembrane integrin receptors anchor the actin cytoskeleton to focal adhesions and transmit information from the extracellular environment. Several PDZ-LIM proteins have been localized to focal adhesions, providing the possibility that Pdlim7 could similarly engage with proteins clustered in focal adhesions including integrin receptors to sense extracellular stress.