Fig. 1.
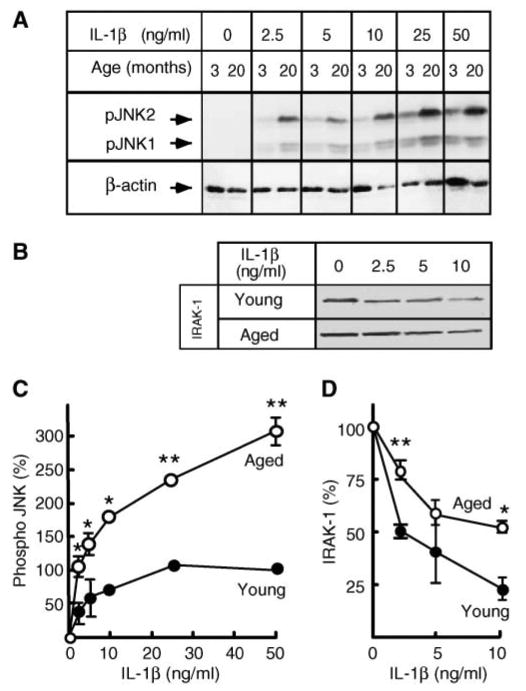
Hepatocytes from aged rats are hypersensitive to interleukin-1β (IL-1β). A, C: Dose response of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation. Hepatocytes from young (3–4 months) and aged (20–22 months) rats were treated with the indicated concentrations of IL-1β for 15 min. JNK phosphorylation was determined by Western blotting using an antibody specific for the dually phosphorylated forms of JNK1 and JNK2 (pJNK1/2). β-Actin was used as a control for uniform loading. The combined intensity of JNK1 and JNK2 was used for quantification. Data are presented as percentages of the phospho-JNK levels in young hepatocytes at 50 ng/ml IL-1β. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). * P < 0.01, ** P < 0.001. B, D: Dose response of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1) degradation. Hepatocytes from young (3–4 months) and aged (20–22 months) rats were treated with the indicated concentrations of IL-1β for 15 min. Levels of IRAK-1 were determined by Western blotting and quantified. Results are expressed as percentages of the IRAK-1 levels in untreated hepatocytes. Values are means ± SD (n = 3). * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.005.
