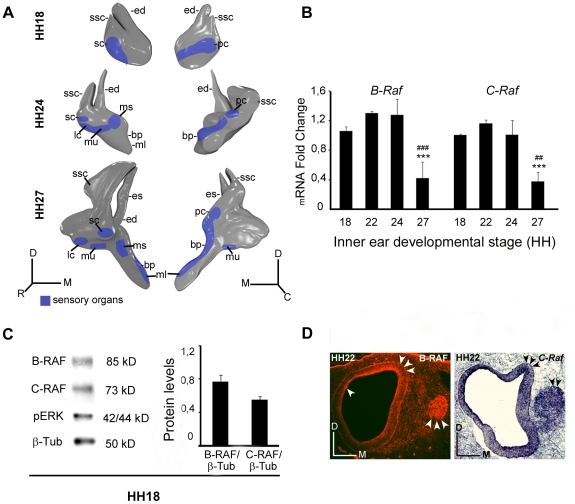
Figure 1. Expression of the B-RAF and C-RAF kinases during otic development.
(A) Schematic drawings showing the development of the chicken inner ear at Hamburger and Hamilton stages HH18, HH24 and HH27. (B) Expression of inner ear B-Raf and C-Raf mRNA analyzed by qRT-PCR at different stages using Eukaryotic 18S rRNA as the endogenous housekeeping control gene. Gene expression was calculated as 2−ΔΔCt and normalized to the levels at HH18. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Statistical significance was estimated with the Student's t-test: ***P<0.005 versus HH18, ##P<0.01 versus HH24 and ###P<0.005 versus HH24. (C) HH18 otic vesicle lysates analyzed in western blots to determine the levels of B-RAF, C-RAF and phosphorylated ERK (pERK). ß-Tubulin (ß-Tub) was used as a loading control. A representative blot of three independent experiments is shown and the average densitometric measurements of the B-RAF and C-RAF bands are plotted as bars. The results are given as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. (D) Immunofluorescence of B-RAF and in situ hybridization of C-Raf at HH22 and HH24, respectively showing their location in the otic epithelium and acoustic-vestibular ganglion (arrowheads). Abbreviations: bp, basilar papilla; ed, endolymphatic duct; es, endolymphatic sac; lc, lateral crista; ml, macula lagena; ms, macula sacculi; mu, macula utriculi; pc, posterior crista; sc, superior crista; ssc, superior semicircular canal. Orientation: C, caudal; D, dorsal; M, medial; R, rostral.