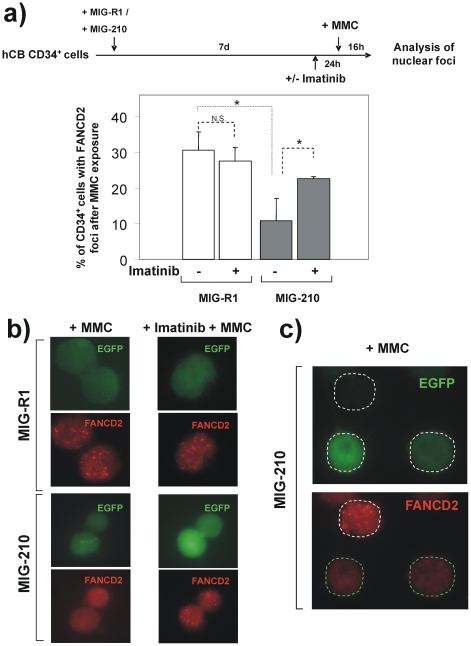
Figure 2. Direct effect of BCR/ABL upon the formation of nuclear FANCD2 foci in human cord blood CD34+ cells.
a) Experimental protocol and analysis of the proportion of cord blood CD34+ cells with FANCD2 nuclear foci after transduction with retroviral vectors expressing EGFP (MIG-R1) or EGFP plus BCR/ABL (MIG-210). The effect of imatinib upon the formation of FANCD2 foci in these cells is also shown. In all instances cells were treated with MMC (40 nM) 16 h prior to conduct the immunofluorescence studies. Bars show mean ± s.e. of values corresponding to three independent experiments. *Differences were significant at p<0.01. b) Representative pictures showing restored formation of FANCD2 nuclear foci in MIG-210-transduced CD34+ cells treated with imatinib. Nuclear foci were exclusively scored in cells expressing the retroviral vector marker gene (EGFP). c) Representative pictures showing the specific inhibition of FANCD2 foci in human CD34+ cells transduced with MIG-210. Note that only cells expressing the marker EGFP, co-expressed with BCR/ABL in this vector, are negative for FANCD2 foci.