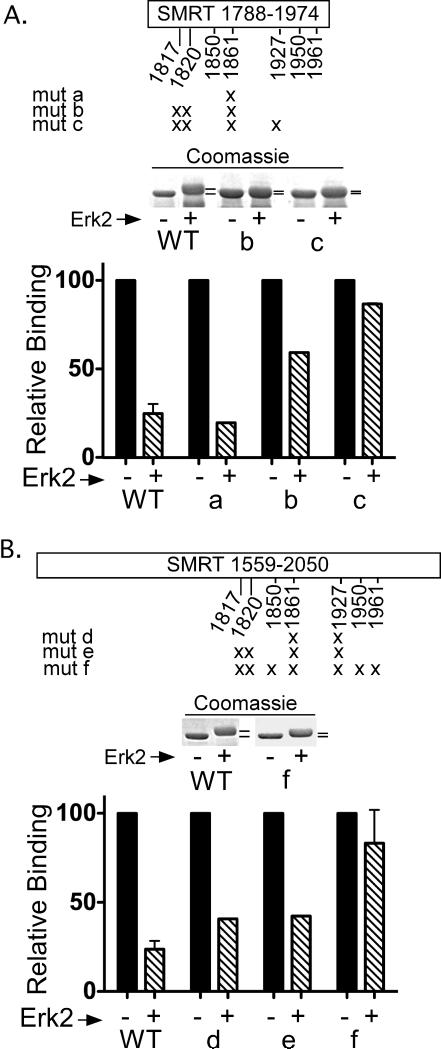
Figure 5. A cluster of Erk2 phosphorylation sites regulate SMRTα self-association.
A. A schematic of the SMRTα (1788-1974) domain is presented; 7 Erk consensus phosphorylation sites (S/T-P) are highlighted. Mutant constructs bearing alanine substitutions at these positions (“X”) are indicated. The ability of the wild-type or mutant GST-SMRTα (1788-1974) construct to be shifted in mobility by incubation with Erk2 (middle panel) and to bind full-length 35S-SMRTα in a GST-pulldown (bottom panel) were determined as in Figure 4. B. The analysis of Erk2 phosphylation sites was extended to the larger SMRTα (1559-2050) domain, using the same methodology as in panel A.