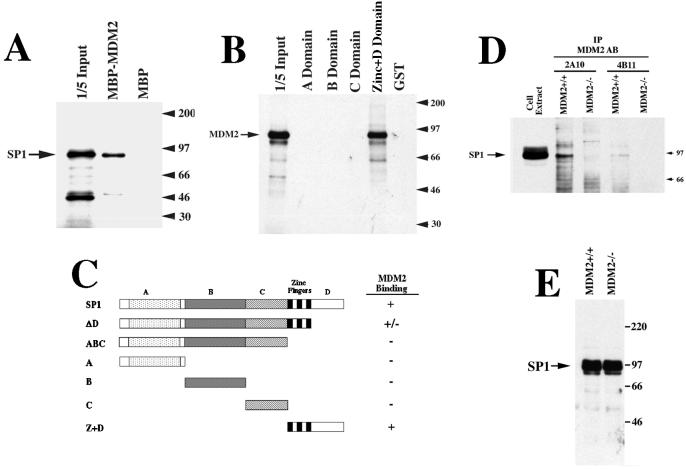
Figure 2.
Physical association between MDM2 and Sp1 in vitro and in vivo. (A) In vitro-translated Sp1 binds to MBP-MDM2. Radiolabeled Sp1 was incubated with MBP-MDM2 alone, and visualized after PAGE. (B) In vitro-translated MDM2 binds to GST-Sp1. Radiolabedled MDM2 was incubated with different GST-Sp1 constructs and subjected to a GST-puldown assay. GST-A, -B, and -C domain fusion proteins, as well as the GST-zinc + D domain were described previously (34). (C) Schematic representation of the Sp1 deletion constructs used in the MBP or GST pulldown assays. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation of Sp1 with two different MDM2 antibodies. Cell extracts from MDM2+/+ or MDM−/− cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with the MDM2 antibodies 2A10 and 4B11 (5); bound proteins were subjected to immunoblot analysis with an antibody against Sp1. Sp1 immunoreactivity is detected only in cells that contain an intact MDM2 gene. (E) Expression of endogenous Sp1 is similar in MDM2+/+ and MDM2−/− cells. Western blot hybridization, using an antibody against Sp1, on the cell extracts used in D above.