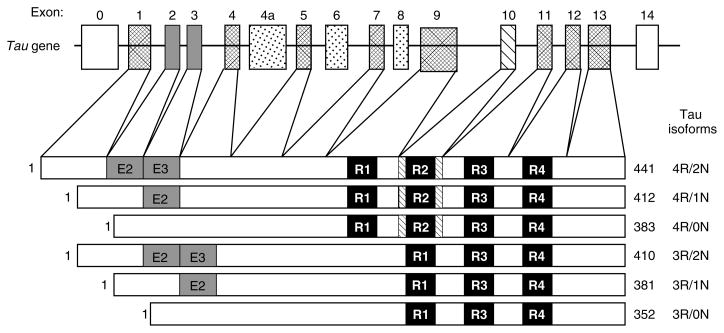
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of the human tau gene and six human CNS tau isoforms generated by alternative splicing. The human tau gene contains 16 exons, including exon 0 that is part of the promoter. Exons 1, 4, 5, 7, 9, and 11–13 are constitutively expressed. Alternative splicing of exons 2 (E2), 3 (E3), and 10 produces the six alternative tau isoforms. Exons 6 and 8 are not transcribed in the human CNS. Exon 4a, which is also not transcribed in the human CNS, is expressed in the PNS leading to the larger tau isoforms, termed ‘big tau’. The black bars depict the 18 amino acid MT binding repeats and are designated R1 to R4. The relative sizes of the exons and introns are not drawn to scale