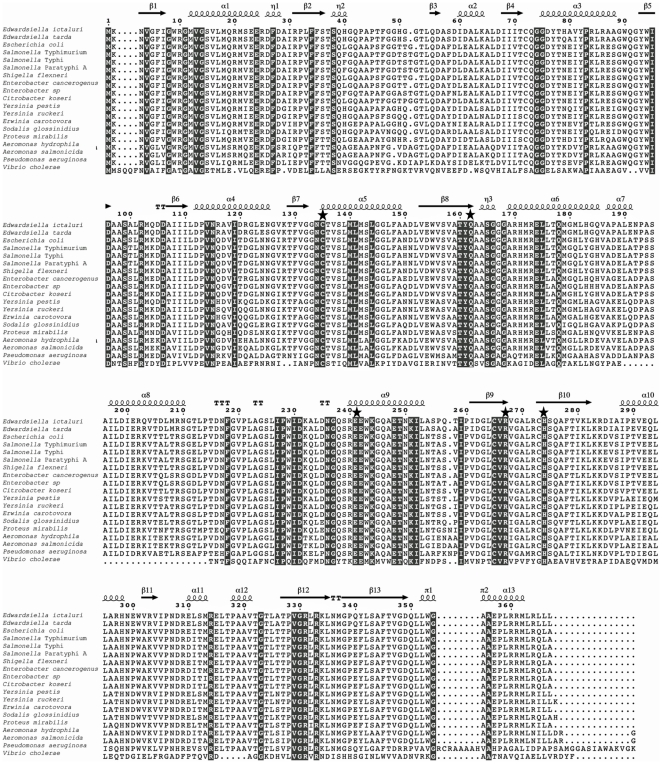
Figure 1. Sequence alignment among representative members of the AsdA family.
The secondary structure at the top of the alignment corresponds to the E. ictaluri AsdA enzyme (spirals represent α-helix; arrows represent β-sheet). Conserved amino acids residues are indicated in grey. The stars indicated the key catalytic active site residues (Cys-135, Gln-162, Glu-241, Arg-267, and His-274). The AsdA sequences were obtained from NCBI's Entrez Protein database for Edwardsiella ictaluri YP_002935083.1; Edwardsiella tarda YP_003297386.1; Escherichia coli AP_004358.1; Salmonella Typhi NP_807591.1; Salmonella Paratyphi A YP_152515.1; Salmonella Typhimurium AAB69392.1; Shigella flexnieri YP_690789.1; Shigella sonnei YP_312455.1; Citrobacter koseri YP_001456333.1; Enterobacter cancerogenus ZP_05969786.1; Enterobacter sp. YP_001178547.1; Yersinia pestis NP_671174.1; Yersinia ruckeri ZP_04615435.1; Proteus mirabilis YP_002152826.1; Aeromonas hydrophila ABK39477.1; Aeromonas salmonicida YP_001142146.1; Sodalis glossinidius YP_456010.1; Vibrio cholerae YP_001217562.1; Pseudomonas aeruginosa NP_251807.1; Erwinia carovora atrosepticum YP_052242.1.