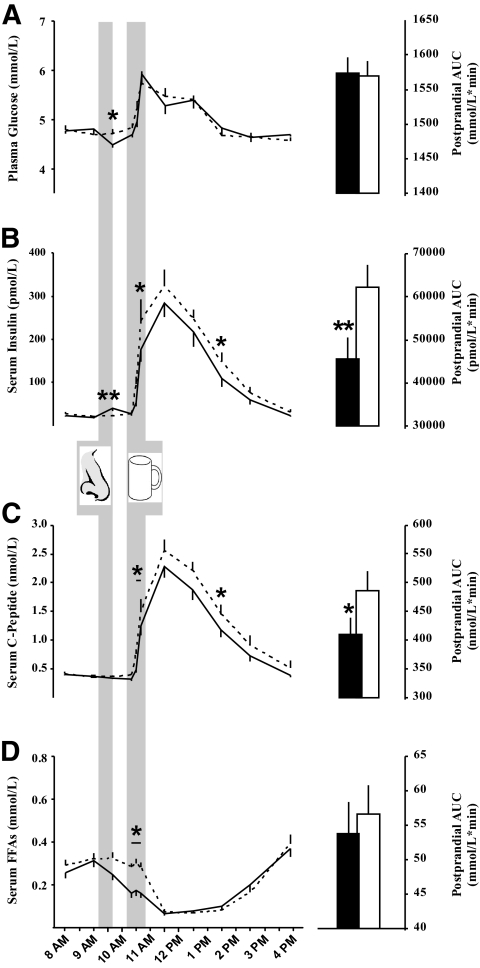
FIG. 3.
Intranasal insulin lowers postprandial serum insulin levels. Concentrations of plasma glucose (A), serum insulin (B), serum C-peptide (C), and serum free fatty acids (D) before and after acute intranasal administration (nose symbol) of intranasal insulin (160 IU; solid lines and black bars) and placebo (dashed lines and white bars) followed by the standardized ingestion of 900 kcal of liquid food (cup symbol). Postprandial levels (10:20 a.m.–4:00 p.m.) were also expressed as AUCs (right panels). All values are presented as means ± SEM. N = 19. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.