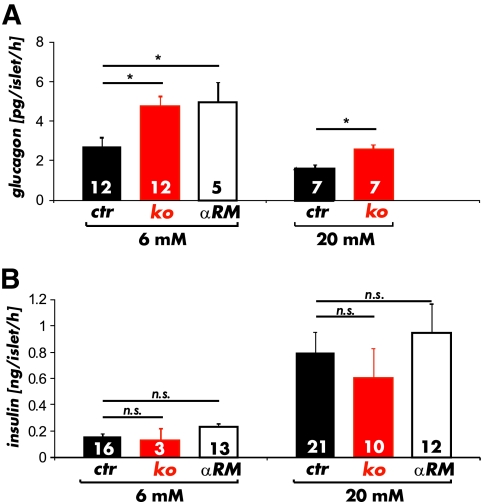
FIG. 4.
Insulin and glucagon release from intact islets. A: Glucagon release from isolated cGKI-KO (KO) islets (red bars) and αRM islets (open bars) was increased at 6 mmol/l as compared with isolated control islets (black bars). Although control and cGKI-KO islets were able to decrease glucagon secretion at 20 mmol/l glucose, the glucagon release was yet significantly higher in cGKI-deficient (red bars) islets. (*P < 0.05). B: Insulin release from isolated cGKI-KO (KO) and αRM islets was unchanged at high (20 mmol/l) and basal (6 mmol/l) glucose concentrations compared with control (CTR) islets. (A high-quality color representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)