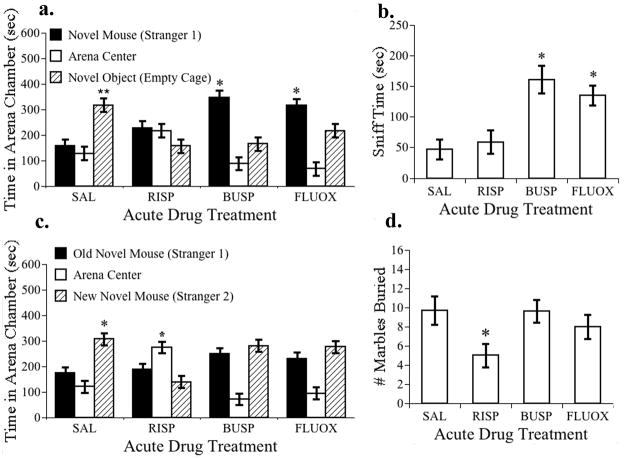
Figure 4. Effect of acute drug treatments on the behavior of BTBR mice in tasks relevant to core behavioral symptoms of ASD.
The effects of acute saline (SAL), risperidone (RISP, 0.1 mg/kg), buspirone (BUSP, 2 mg/kg) or fluoxetine (FLUOX, 10 mg/kg) administration on BTBR mouse behavior. N=8 per treatment. (a) Buspirone and fluoxetine significantly increased sociability in BTBR mice. Time spent by subjects in the arena box containing the stranger mouse was significantly greater than the time spent in the box containing a novel empty cage (*, p < 0.05). Saline-treated BTBR mice exhibited no preference for sociability and spent significantly more time in the box with the novel object and less time in the box with the stranger than either buspirone or fluoxetine treated mice (**, p< 0.05). (b) Buspirone and fluoxetine treatments increased the time spent by BTBR mice sniffing the stranger mouse in the social interaction test relative to saline-treated controls (*, p<0.05). (c) In the test for social novelty, only the saline-treated mice spent proportionally more time in the box containing the new mouse (stranger 2) relative to the box containing the old novel mouse (stranger 1) (*, p<0.05). (d) Marble burying by BTBR mice was reduced by risperidone treatment (*, p<0.05).