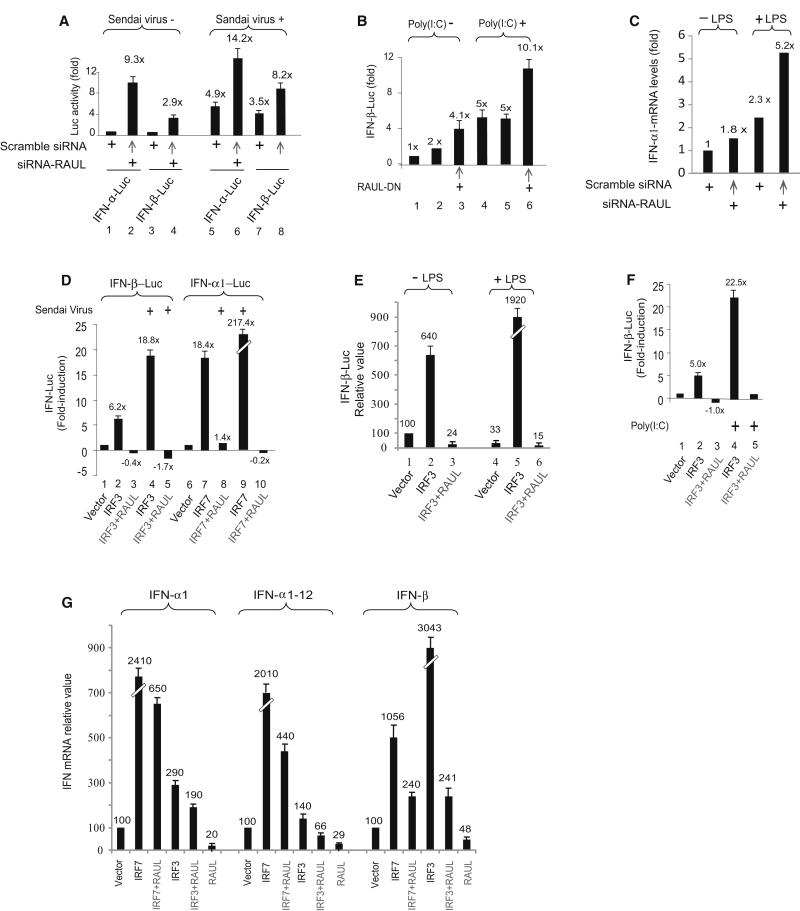
Figure 4. RAUL negatively regulates IRF7 and IRF3-mediated type 1 IFN production.
(A, B and C): Suppression of RAUL by siRNA or dominant negative augments type 1 IFN activity. (A): Luciferase assay of 293T cells transiently expressing siRNA-RAUL together with IFN-α1 or IFN-β luciferase reporter plasmids. The cells were infected with Sendai virus for 16 hr before harvest. The basal IFN-α and IFN-β activities were arbitrarily set to 1.0. (B): Luciferase assay of IFN-β promoter activity from 293-TLR3 cells transiently expressing dominant negative RAUL poly I:C (25 μg/ml) for 9 hr to activate IRF3. (C): Silencing of RAUL increases IFN-α1 mRNA in dendritic cells. DC 2.4 cells were electroporated with siRNA-RAUL or scrambled siRNA in the presence or absence of LPS. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to SYBR green Real time RT-PCR with primers for IFN-α1. (D, E and F): Enforced RAUL expression abolishes IRF7 and IRF3-mediated type I IFN induction under Sendai virus or LPS or poly I:C stimulation. The indicated cells were cotransfected with IFN-α1 or IFN-β luciferase reporters, IRF7 or IRF3 and RAUL and the indicated cells were infected with Sendai virus (16 hr) or stimulated by LPS (100 ng/ml, for 9 hr) or poly I:C. IFN promoter activation was determined by luciferase assay. G: RAUL inhibits IRF7 or IRF3-mediated type I IFN mRNA production. 293T cells were cotransfected with IRF7, IRF3 and RAUL plasmids as indicated. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to SYBR green Real time RT-PCR with primers for IFN-α1, IFNα-1-12 and IFN-β, respectively, to assess type 1 IFN mRNA output.