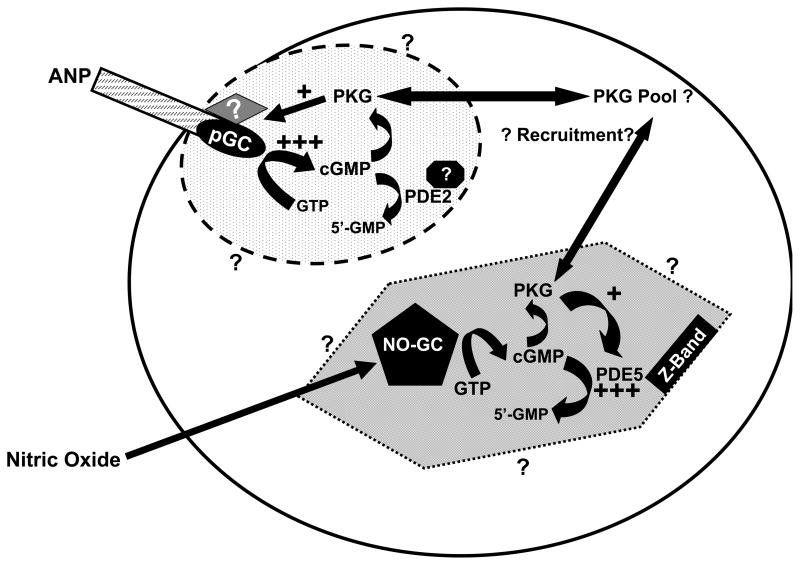
Figure.
Diagram depicting effect of activation of PKG on cGMP synthesis and breakdown in cardiomyocytes. The cGMP pools are indicated by the oval and hexagon containing cGMP-signaling proteins. Dotted boundaries indicate that these pools are restricted, but not impermeable; surrounding question marks indicate that spatial dimensions of the pools are poorly understood. ANP activation of pGC increases cGMP production in the subsarcolemmal region resulting in PKG activation. The activated PKG acts on ANP-activated pGC to increase cGMP synthesis (+++) and generate feed-forward regulation. The diamond with a question mark indicates that the target of PKG could be a protein that influences pGC activity and/or ANP sensitivity. Interactions that localize PDE2 to this region are unknown and indicated by the approximated black octagon. NO-activation of the NO-GC increases cGMP synthesis in the cytosolic pool; PKG activated by the increase in cGMP phosphorylates/activates PDE5 (+++), which rapidly hydrolyzes cGMP resulting in negative feedback regulation of cGMP in this pool.