Figure 4.
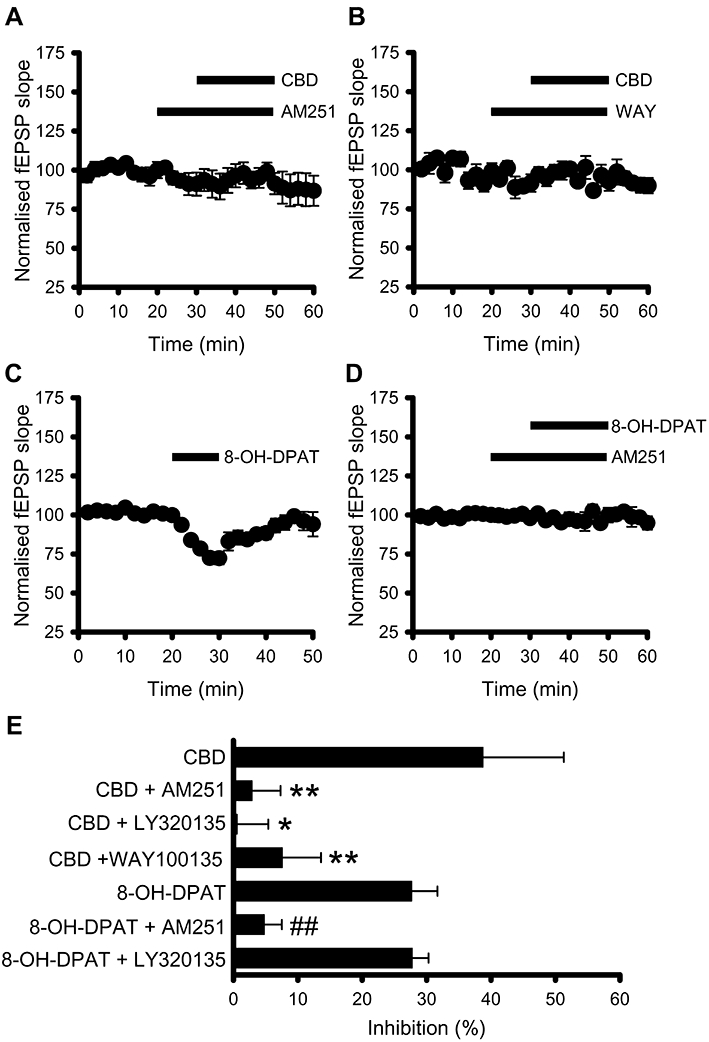
Cannabidiol (CBD)-mediated inhibition of synaptic transmission in acute hippocampal slices is sensitive to 5-HT1A and cannabinoid receptor (CB1) antagonism. (A) CBD (10 µM)-mediated inhibition of synaptic transmission was abolished by the proposed CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 (2 µM). (B) Inhibition of transmission by CBD was significantly reduced in the presence of the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, WAY100135 (300 nM). (C) 8-OH-DPAT (10 µM) reversibly inhibits field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSP). (D) AM251 (2 µM) inhibits the 8-OH-DPAT (10 µM)-mediated inhibition of fEPSPs. (E) Summary data showing that CBD-mediated effects were significantly reduced in the presence of 5-HT1A and CB1 receptor antagonists. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with CBD alone. ##P < 0.01 compared with 8-OH-DPAT alone.
