FIGURE 6. Identification of an essential leucine residue in three PCI domains.
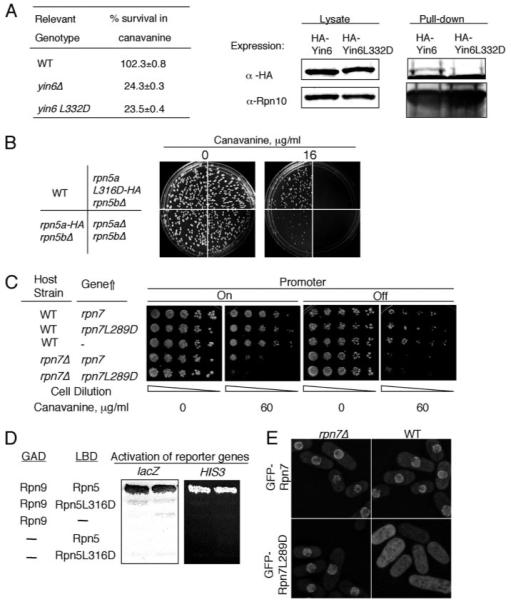
A, left, various strains were pregrown in YEAU at 30 °C to log phase. Equal numbers of cells were spread on MM plates without or with 12 μg/ml canavanine sulfate and incubated at 30 °C for 14 days. For each strain, the number of colonies that emerged on plates without canavanine was taken as 100% survival. The specific strains used were SP870 (WT), YIN6K (yin6Δ), and YIN6LD (yin6L332D). Right, cells whose Rpn10 is tagged with protein A were transformed with pHA-YIN6 or pHA-YIN6LD, and lysates were prepared and pulled down with either IgG or control protein A beads. The pulled-down proteins were analyzed by Western blots using antibodies specific for either HA or Rpn10. B, there are two copies of rpn5 genes, rpn5a and rpn5b. Equal numbers of cells from strains with the indicated genotype were spread on MM plates containing the indicated concentration of canavanine sulfate. The plates were incubated at 30 °C. The specific strains used for this study were as follows (see “Experimental Procedures” and Ref. 14): SP870 (WT), RPN5LD (rpn5aL316D-HA rpn5bΔ), RPN5bARPN5aHA (rpn5a-HA rpn5bΔ), and RPN5UA (rpn5aΔ rpn5bΔ). C, WT or rpn7Δ cells were transformed with the vector control (–, pREP41) or the same vector expressing the indicated genes (pREP41Rpn7 and pREP41RPN7LD). The transformed cells were then serially diluted and spotted on MM plates containing the indicated concentration of canavanine and incubated at 30 °C for 5 days. The expression of the gene was turned off by adding thiamine (20 μM). D, hybrid proteins fused with the LexA DNA binding domain (LBD) and the Gal4 activation domain (GAD) are as indicated, and the activation of both HIS3 and lacZ is shown. The plasmids used for expressing these fusion genes are pGADRPN9, pLBDRPN5, and pLBDRPN5LD. E, WT or rpn7Δ cells were transformed with linearized pREPGF-PRPN7 or pREPGFPRPN7LD to allow integration of these plasmids to the chromosome. These cells were grown in YEAU at 30 °C to log phase before being photographed. The images were captured under identical conditions to reveal the different intensities of GFP signals between samples.
