FIGURE 7. The function of the identified Leu is conserved.
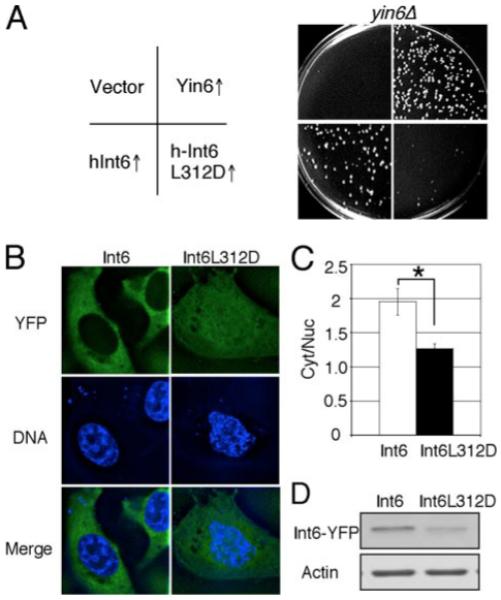
A, the same number of yin6Δ cells (strain YIN6K) transformed with a vector control (pSLF173) or the same vector carrying the indicated genes (pHAYIN6, pHAHINT6, and pHAHINT6LD) were spread on MM plates and incubated at 20 °C for 6 days. The growth of wild-type cells was unaffected by wild-type or mutated yin6 expression (data not shown). B, HeLa cells were transiently transfected with vectors expressing the indicated proteins that were YFP-tagged. The DNA was stained by Hoechst 33342 to mark the nucleus. Images were deconvolved. YFP and DNA signals in the same focal plane are shown and merged. C, the ratios of cytoplasmic versus nuclear YFP signal intensity in the cell were calculated from six cells (*, p < 0.05). D, ectopically expressed Int6 proteins were examined by Western blots, and β-actin was examined as loading control. Int6L312D was expressed at a level lower than that of wild type Int6, thus ruling out the possibility that its mislocalization is simply due to gross overexpression. The plasmids used to express wild-type or mutant int6 in HeLa cells were pYFPHINT6 and pYFPHINT6LD, respectively.
