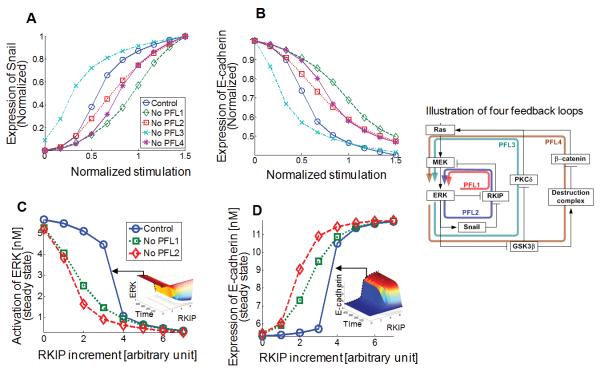
Figure 5. CPFLs cooperatively induce a switch-like behavior of cellular responses and RKIP determines ERK activation and E-cadherin suppression.
(A) Snail expression in response to normalized EGF simulation. (B) E-cadherin expression. ‘Control’ denotes the case when all PFLs are connected and ‘No PFLi’ (i=1,…,4) indicates the case when PFLi is removed. Within a certain range of concentration values of RKIP a switch-like behavior of cellular responses is observed. This switch-like behavior disappears, if one of the CPFLs mediated by RKIP is blocked. (C) The activation profile of ERK. (D) The expression profile of E-cadherin. The right inset shows the illustration of four feedback loops through which the ERK signaling pathway is regulated through: ERK RKIP MEK → ERK (PFL1), ERK →Snail RKIP MEK → ERK (PFL2), ERK GSK3β PKCδ → Ras → ERK (PFL3), ERK GSK3β → Destruction complex β-catenin→ Ras → ERK (PFL4).