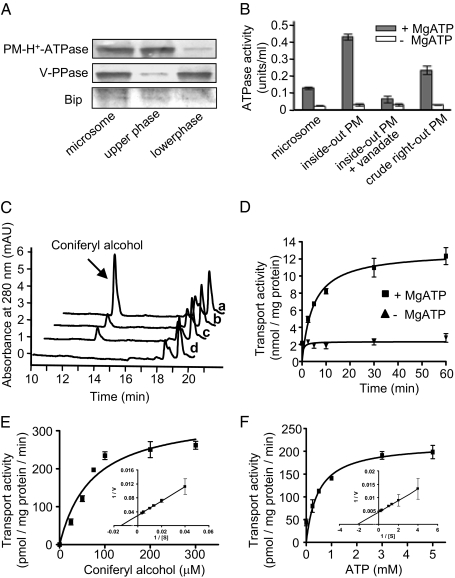
Fig. 1.
Preparation and characterization of plasma membrane (PM) vesicles and the transport of monolignols by inside-out plasma membrane vesicles. (A) Protein gel-blot analysis of membrane fractions by probing with antibodies against Arabidopsis plasma membrane H+-ATPase (PM-H+-ATPase), vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase (V-PPase, tonoplast marker), and endoplasmic reticulum-binding protein (Bip, ER marker). (B) H+-ATPase activities of different membrane preparations in the presence or absence of MgATP. The results are from three replicates. (C) Portions of HPLC traces showing the recovered coniferyl alcohol from the inverted vesicles in the uptake assay in the presence (a) and absence (b) of ATP, the presence of sodium vanadate and ATP (c), and the absence of phenolic substrate (d). (D) Time course of the transport of coniferyl alcohol into the inside-out vesicles. The results are the mean and SD of two replicates. (E and F) The kinetics of transport of coniferyl alcohol into Arabidopsis inside-out plasma membrane vesicles for coniferyl alcohol (E) and MgATP (F) concentrations. The data are plotted by a nonlinear regression analysis fit to the Michaelis–Menten equation. The insets in E and F show Lineweaver–Burk plots. The data are the means and SD of two or three replicates.