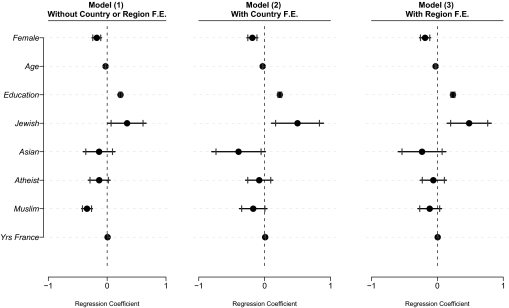
Fig. 1.
Impact of religion and geographic origin on a household's yearly income. This figure is based on results in Table S1. The dependent variable is an ordinal variable ranging from the value “0” if the yearly household income is null to “14” if the yearly household income is greater than 68,000 Euros. The independent variable is whether the respondent is “Muslim,” a binary variable, which takes the value “1” if the head of household is Muslim and “0” otherwise. In model 1, Muslim is significant at the P < 0.01 significance level on a two-tailed test. It is not significant by conventional standards in model 2 and in model 3. As for controls, “Female” is a binary variable, which takes the value “1” if the head of household is female and “0” if the head of household is male. “Age” is a continuous variable equal to the actual age of the head of household. “Education” is an ordinal variable ranging from the value “1” for no schooling to “6” for postsecondary education. “Jewish” is a binary variable, which takes the value “1” if the head of household is Jewish and “0” otherwise. “Asian” is a binary variable, which takes the value “1” if the head of household is Buddhist, Hindu, Shintoist, or Confucianist and “0” otherwise. “Atheist” is a binary variable, which takes the value “1” if the head of household is an atheist and “0” otherwise. The reference group is “Christian,” a binary variable, which takes the value “1” if the head of household is Christian and “0” otherwise. “Yrs France” is a continuous variable equal to the number of years that the head of household has lived in France. SEs in the original probit model are robust. In the figure, the dot represents the regression coefficient, the horizontal line marks the 95% confidence level, and the two vertical lines mark the 90% confidence level. F.E. refers to fixed effects.