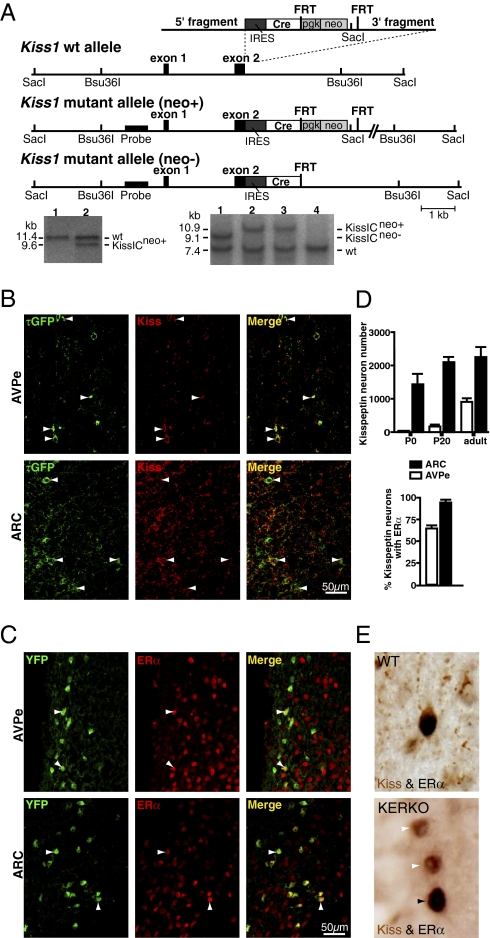
Fig. 1.
Conditional ERα knockout in kisspeptin cells. (A) Targeting strategy to express Cre recombinase under control of the Kiss1 promoter. The targeting vector, the WT alleles, and the targeted allele before (neo+) and after (neo−) removal of the neomycin selection cassette are shown from top to bottom. Restriction sites used for Southern blot analysis, as well as the location of the probes, are indicated. Black boxes represent exons. The inserted cassette is composed of an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES) followed by the coding sequence for Cre recombinase (Cre), and a phosphoglycerate kinase promoter-driven neomycin resistance cassette flanked by Flp recombinase recognition sites (FRT). Southern blot analysis of ES-cell DNA after digestion with SacI. The expected fragment sizes detected by the probe are indicated (WT, 11.4 kb; mutant, 9.6 kb). Clone 2 carries the mutant KissI allele (KissICneo+). Southern blot analysis of DNA digested with Bsu36I from WT, and heterozygous mutant mice before and after removal of the neomycin selection cassette. The expected fragment sizes detected by the probe are indicated (WT, 7.4 kb; mutant allele I KissICneo+, 9.1 kb; mutant allele II KissICneo−, 10.9 kb). Mice 2 and 3 carry mutant allele I (KissICneo+), mouse 1 carries mutant allele II after Flp recombinase mediated excision of the neomycin cassette (KissICneo−). (B) Cre-mediated recombination is restricted to kisspeptin neurons. τGFP+ neurons were found in the ARC and AVPe of female KissIC/eR26-τGPF (green) mice. Immunofluorescence analysis of ARC and AVPe sections using antibodies against kisspeptin shows that >95% of kisspeptin containing cells (red) display τGFP fluorescence (green), demonstrating faithful activation of the ROSA26-τGFP reporter gene in kisspeptin neurons. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (C) ERα expression in kisspeptin neurons. Immunofluorescence analysis of ARC and AVPe sections from female KissIC/R26-YFP mice using antibodies against ERα shows that most ARC and AVPe kisspeptin neurons (green) express ERα (red). (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (D) Differential onset of kisspeptin expression in the AVPe and ARC. Number of kisspeptin neurons (YFP+) in the AVPe and ARC of female KissIC/R26-YFP mice on the day of birth (P0) and before (P20) and after (adult) puberty. Percentage of kisspeptin neurons expressing ERα in the AVPe and ARC of adult female KissIC/R26-YFP mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. (E) Conditional ERα knockout in kisspeptin neurons confirmed by dual labeling of ERα (black nuclear staining) and kisspeptin (brown cytoplasmic staining). (Upper) Double-labeled ERα-kisspeptin neuron in the AVPe of a WT mouse. (Lower) Two kisspeptin neurons lacking ERα immunoreactivity and one nonkisspeptin immunoreactive neuron expressing ERα in the AVPe of a KERKO mouse.