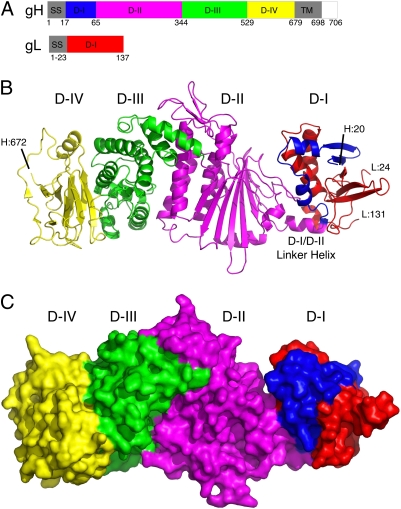
Fig. 1.
Structure of EBV gH and gL heterodimer. (A) Schematic diagram of the EBV gH and gL domain structures. Colored domains correspond to the crystal structure shown in B. Regions not in the construct are colored gray or white. Sequence numbers are indicated below. (B) Ribbon diagram of the EBV gH/gL structure. gH is colored blue in D-I, magenta in D-II, green in D-III, and yellow in D-IV. gL is colored red. The D-I/D-II linker helix and the gH and gL N- and C-terminal residues are indicated, with L:24 and L:131 referring to gL residues 24 and 131 and H:20 and H:672 referring to gH residues 20 and 672. At the N terminus of gH and not visible in the structure were residues AMT that were added to the soluble protein as a result of cloning. Similarly, for gL, N-terminal residues AMD (from cloning) were not observed in the structure. At the C terminus, gH residues 673–679 and gL residues 132–137 were not observed. (C) Surface of the EBV gH/gL structure colored by domain as in B.