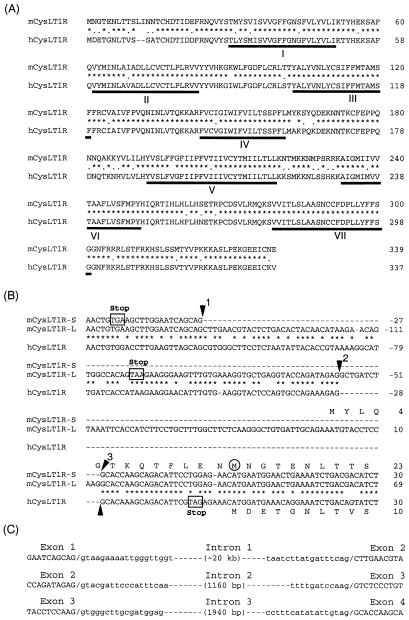
Figure 1.
Structure of the cDNA and the gene for the mouse CysLT1 receptor. (A) Alignment of amino acid sequences of the mouse (short isoform) (mCysLT1R) and the human (hCysLT1R) CysLT1 receptors. Asterisks and dots indicate identical and similar amino acids in the mouse and the human CysLT1 receptors, respectively. Seven putative transmembrane domains (I–VII) are underlined. (B) Alignment of the nucleotide sequences of the partial 5′ noncoding and coding regions of the mouse short isoform (mCysLT1R-S), the mouse long isoform (mCysLT1R-L), and the human CysLT1 receptor (hCysLT1R) cDNA. Asterisks indicate identical nucleotides in the mouse and the human. The exon/intron junctions in the mouse and the human (11) (GenBank accession no. AC021992) CysLT1 receptor genes are indicated by numbered arrowheads. In-frame stop codons are shown by open boxes. The start methionine in the short isoform of the mouse cDNA is circled. For the long isoform cDNA, exon I is 5′ of arrow 1, exon II is between arrows 1 and 2, exon III is between arrows 2 and 3, and exon IV is 3′ of arrow 3. Note that the hCysLT1R is missing the equivalent of mouse exon III. (C) Boundary sequence of the four exons and the sizes of the three introns of the mCysLT1R-L.