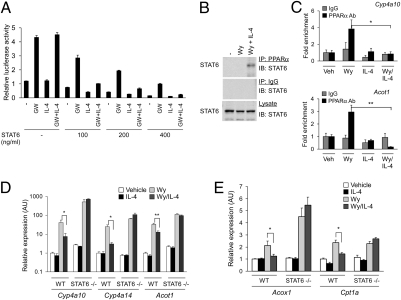
Fig. 2.
IL-4 and STAT6 inhibit PPARα transcriptional activity. (A) Suppression of PPARα transcriptional activity by STAT6 and IL-4. CV-1 cells were transfected with reporter plasmid (PPRE3-tk-Luc, 100 ng) and expression plasmids for PPARα (25 ng) and STAT6 (varying amounts). (B) Coimmunoprecipitation of STAT6 and PPARα. Liver lysates from treated animals were immunoprecipitated with anti-PPARα antibody and immunoblotted for STAT6. (C) ChIP analysis of PPARα target genes. Chromatin fragments were precipitated from hepatocytes treated with vehicle or Wy14643 (Wy) in the presence or absence of IL-4. Regions flanking the PPARα binding sites on Cyp4a10 and Acot1 promoters were amplified by qPCR and data were normalized to IgG control. (D and E) Activation of STAT6 by IL-4 represses PPARα transcriptional activity. Quantitative RT-PCR analyses of PPARα target genes in primary hepatocytes. Error bars are displayed as mean ± SEM (n = 3–4 for each mouse group). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.