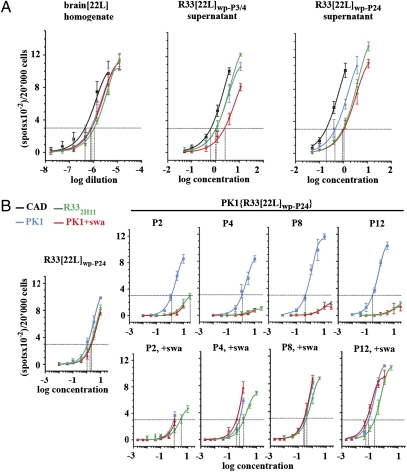
Fig. 1.
Transfer of prions from R33[22L]wp cells to PK1 cells entails a change in the CPA profile. (A) R33 cells were infected with a 10−3 dilution of 22L-infected brain homogenate for 4 d and propagated for three and four 1:20 splits to yield the uncloned populations R33[22L]wp-P3 and R33[22L]wp-P4, respectively. Conditioned media from the two cultures were combined. The R33[22L]wp population was propagated further for a total of twenty-four 1:20 splits to yield R33[22L]wp-P24. (B) PK1 cells were exposed to 20× concentrated conditioned medium from R33[22L]wp-P24 cells for 4 d and propagated in the presence or absence of 2 μg swa/mL for twelve 1:20 splits. In all cases conditioned media were concentrated 200-fold and assayed by the SSCA on PK1 cells with or without swa and on CAD and R332H11 cells. There was no change in properties of the prions secreted by the R33[22L]wp population even after 24 splits (A). After transfer to PK1 cells, the prions progressively lost R33 competence and swa resistance when cells were propagated in the absence of swa (B, Upper). However in the presence of swa (B, Lower), R33 competence and swa resistance were retained.