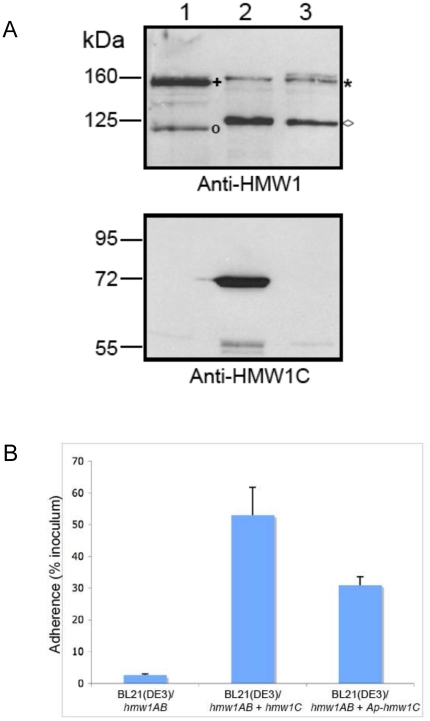
Figure 5. Ability of ApHMW1C to complement a deficiency in HMW1C.
Panel A shows Western immunoblots of whole cell sonicates of E. coli BL21(DE3)/pACYC-HMW1ΔC (lane 1), E. coli BL21(DE3)/pACYC-HMW1ΔC + pET45b-HMW1C (lane 2), and E. coli BL21(DE3)/pACYC-HMW1ΔC + pET45b-ApHMW1C (lane 3). Lane 1 contains twice as much protein as loaded in lanes 2 and 3 to increase the visibility of the non-glycosylated HMW1 species. The blot in the upper panel was performed with a guinea pig antiserum reactive with HMW1, and the blot in the lower panel was performed with a guinea pig antiserum reactive with H. influenzae HMW1C. The asterisk indicates the glycosylated HMW1 pro-protein, and the plus sign indicates the non-glycosylated HMW1 pro-protein. The diamond indicates the glycosylated HMW1 mature protein, and the circle indicates the non-glycosylated HMW1 mature protein. Panel B shows in vitro adherence results comparing adherence by E. coli BL21(DE3)/pACYC-HMW1ΔC (hmw1AB), E. coli BL21(DE3)/pACYC-HMW1ΔC + pET45b-HMW1C (hmw1AB + hmw1C), and E. coli BL21(DE3)/pACYC-HMW1ΔC + pET45b-ApHMW1C (hmw1AB + Aphmw1C) to Chang epithelial cells. Bars and error bars represent mean and standard error measurements from a representative assay with measurements performed in triplicate.