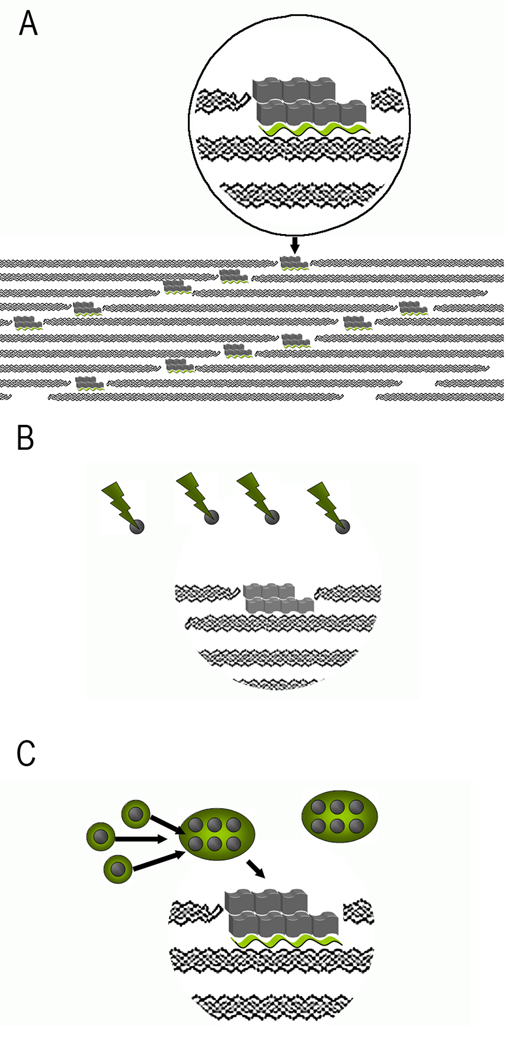
Figure 10.
Models of collagen mineralization. A. Templating of mineral crystals, represented by gray blocks by acidic noncollagenous macromolecules (green wavy ribbons) bound to collagen molecules in the gap region. B. Size exclusion model. Large acidic proteins (green lightening bolts) prevent mineral nucleation (nuclei represented by grey spheres) outside of the fibrils. However, the proteins are too big to fit into the gap regions of the fibrils, where mineral crystals start to grow. C. Protein assemblies (green circles) stabilize the mineral nuclei outside of the fibrils. Upon binding to collagen molecules in the fibril proteins change their conformation, leading to the templated nucleation of mineral crystals in the gap regions.