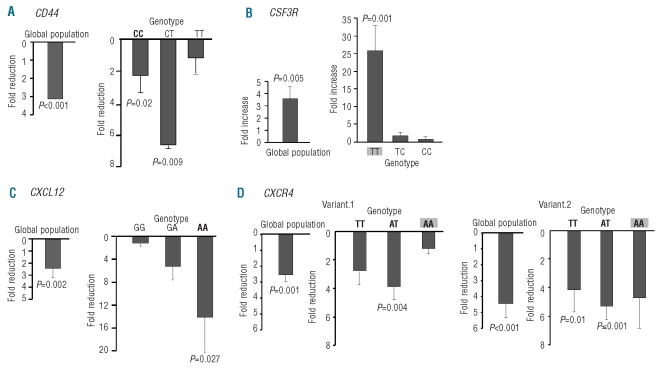
Figure 2.
Effect of G-CSF on mRNA levels of CD44, CSF3R, CXCL12 and CXCR4 in PB. (A) Reduction of CD44 expression in the global population and in the different genotype groups of rs13347 in CD44 after G-CSF. (C) Increase of CSF3R expression after G-CSF in the global population and in the different genotype groups of rs3917924 in CSF3R. (D) Decrease of CXCL12 expression after G-CSF in the global population and in the different genotype groups of rs1801157 in CXCL12. (E) Reduction of expression after G-CSF of CXCR4 variant.1 and variant.2 in the global population and in the different genotype groups of rs2680880 in CXCR4. Shaded and bold genotypes are associated with lower and higher amounts of CD34+ cells in PB after G-CSF administration, respectively. In all the cases, genotype groups at steady sate were used as calibrators. In the case of the global population, the mean of all steady state values was used as a calibrator. For the different genotypes, each genotype after G-CSF was calibrated with the value of the corresponding genotype at steady state. All data were normalized with β-actin. Data are given as mean ± S.E.M. All expression values are linear values relative to the calibrator group. Calibrator groups have a value equal to one; fold reduction or fold increase of the gene expression obtained is relative to that value.