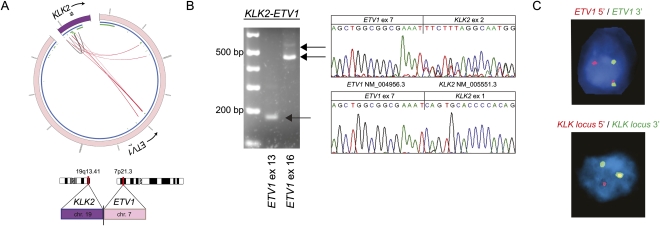
Figure 2.
Identification of KLK2 as novel 5′ fusion partner of ETV1. (A) Circos plot of KLK2–ETV1 rearrangement. Outer ring: (purple) chromosome 19; (pink) chromosome 7. Inner ring: (blue) genes; (green) exons. Within the inner ring, lines denote PE reads with both reads belonging to KLK2 (gray) and reads connecting ETV1 and KLK2 (red). (B) RT-PCR and Sanger sequencing of the resulting fusion transcript reveals the expression of two different fusion transcripts. PCR products were sequenced using the reverse primer, so sequence traces are given in reverse orientation. (C) ETV1 and the KLK locus are rearranged as determined by FISH break-apart assays. Of note, KLK2-specific FISH is not feasible due to the small size of the KLK2 gene and its close location to neighboring genes of the KLK locus. To address this, genomic rearrangement of the KLK2 gene is inferred from a rearrangement in the genomic locus of the KLK gene family.