FIGURE 6.
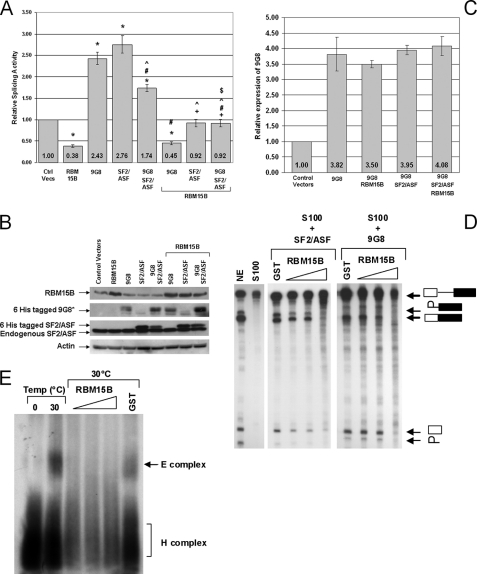
RBM15B suppresses in vivo and in vitro splicing mediated by SR protein SF2/ASF. Expression constructs for RBM15B WT and the SR proteins SF2/ASF and 9G8 were transiently co-transfected with the splicing reporter plasmid pTN24 for 24 h. A, relative splicing activities were calculated using the ratios of luciferase to β-galactosidase activities with the activity of the control cells transfected with empty expression vectors (Ctrl Vecs) set at 1. The results shown represent six independent transfection experiments in which one plate was transfected, and each lysate was measured in quadruplicate. The error bars represent the S.E. Statistically significant comparison data are indicated by the following symbols: *, p < 0.0007 for comparisons with control vectors; +, p < 0.01 for RBM15B with RBM15B/SF2 and RBM15B/9G8/SF2; #, p < 0.01 for 9G8 with 9G8/SF2, RBM15B/9G8, and RBM15B/9G8/SF2; ^, p < 0.01 for SF2 with 9G8/SF2, RBM15B/SF2, and RBM15B/9G8/SF2; and $, p < 0.01 9G8/SF2 with RBM15B/9G8/SF2. B, cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting for expression of the exogenous and endogenous proteins. *, His6-tagged 9G8 was detected by immunoprecipitation from cell lysates using nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid-agarose (Qiagen) and immunoblotting with anti-9G8-ZnK polyclonal antibody. Actin detection demonstrated that equal lysate volume loading resulted in comparable total protein levels. C, overall enforced expression of 9G8 was confirmed by quantitative RT-PCR. D, cytoplasmic S100 cell extract was used for an in vitro splicing assay using the pre-RNA of the human β-globin gene as substrate. S100 extract does not catalyze excision of the β-globin intron without the addition of SR proteins. The accumulation of the mature β-globin spliced product in the presence of HeLa NE (lane 1) is not observed using the S100 fraction alone (lane 2). Addition of 2 pmol/splicing reaction recombinant SF2/ASF (lane 3) or 9G8 (lane 7) proteins to the S100 fraction is sufficient to activate splicing of the β-globin pre-RNA. Increasing amounts (0.5, 2.5, and 5 pmol/splicing reaction) of GST-RBM15B FL protein inhibited the SF2/ASF- (lanes 4–6) and the 9G8-mediated splicing (lanes 8–10), whereas addition of GST alone (5 pmol/splicing reaction; lanes 3 and 7) had no effect. In vitro splicing assays using SF2/ASF were performed with HeLa nuclear extract produced according Mayeda and Krainer (48), whereas splicing reactions with 9G8 were performed using HeLaScribe nuclear extract (Promega). These two extracts differed in splicing activities (supplemental Data S7A). Higher activity was observed in the HeLaScribe as demonstrated by the low abundance of the intermediate splicing product (intron-exon 2). However, RBM15B inhibited splicing with both extracts. E, detection of the spliceosomal complex E was performed using the β-globin substrate and native horizontal agarose minigels. The ATP-independent spliceosomal complex E was detected after a 40-min incubation of the β-globin pre-RNA with HeLa nuclear extract at 30 °C (lane 2). At a temperature of 0 °C (lane 1), this complex did not form. Addition of increasing amounts (0.5, 2.5, and 5 pmol/splicing reaction) of GST-RBM15B FL protein inhibited formation of the E complex at 30 °C, whereas 5 pmol of GST did not affect this splicing step. The H complex is a nonspecific complex resulting from binding of hnRNP proteins to pre-RNAs.