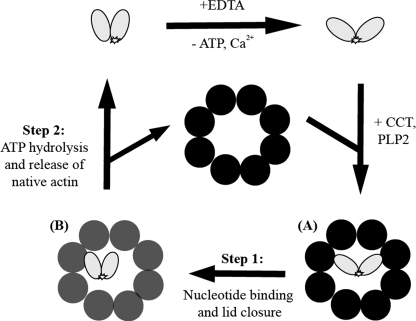
FIGURE 7.
Schematic representation of the proposed model of AcrylAct1 unfolding and binding to CCT. The fluorescent probe is in a more polar environment in native actin than in the EDTA-unfolded intermediate I3 and in the complex with CCT. A, actin binds in a 1,4-conformation across the cavity of the open CCT complex (black) as shown by EM (17). B, binding of ATP or AMP-PNP closes the lid of CCT (gray). Step 1, nucleotide binding induces a conformational change within the actin molecule (24), but does not facilitate release and the environment of the C terminus remains unaffected. Step 2, hydrolysis of ATP is required for the final packing of the actin C terminus and release of native actin from CCT.