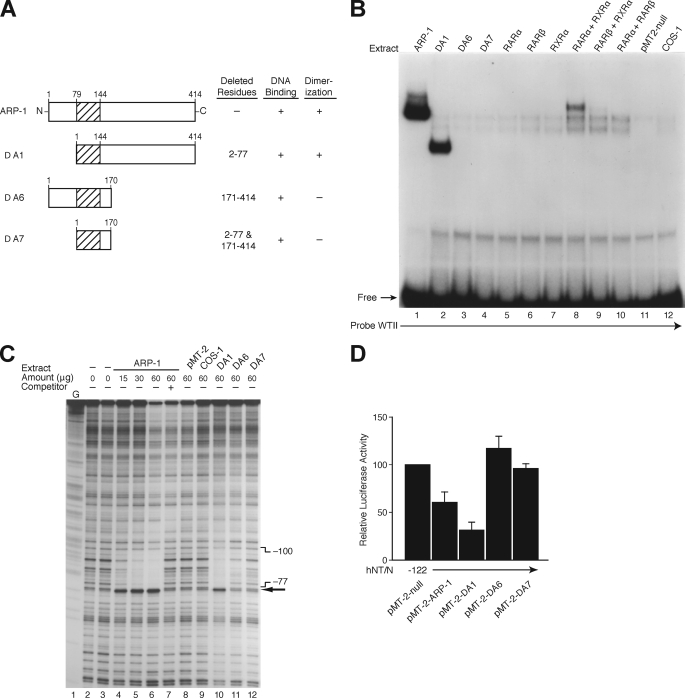
FIGURE 8.
Identification of the functional domains for NR2F2. A, schematic representation of the ARP-1 (NR2F2) deletion mutants used. B, expression plasmids for ARP-1 (NR2F2) and its mutants (Δ1, Δ6, and Δ7) or members of the nuclear receptor superfamily (RARα/β and RXRα/β) and the empty vector, pMT-2-null, were transfected into COS-1 cells. After 48 h, crude protein extracts (20 μg) from transfected or untransfected COS-1 cells were incubated with [32P]ATP-labeled WTII probe for EMSA analysis. C, DNase I footprinting of the NR2F2 site. The coding strand of the hNT/N promoter (−373 to +26) was labeled, incubated with crude protein from COS-1 cells transfected with or without ARP-1 (NR2F2) and its mutants (Δ1, Δ6, and Δ7), and then digested with DNase I. Areas protected from digestion are bracketed with the corresponding nucleotide positions, which were determined by running a DNA sequencing ladder (G reaction) in parallel. The numbers at the top of the autoradiogram are the amounts of nuclear extract (in μg of protein) used in each reaction mixture. A 100-fold molar excess of the oligonucleotide corresponding to the hNT/N promoter fragment −106 to −77 was used as a competitor (lane 7). D, BON cells were co-transfected with the −122 hNT/N promoter plasmid and expression plasmids for NR2F2 (pMT-2-ARP-1) or its deletion mutants (Δ1, Δ6, and Δ7) with the empty vector, pMT-2, and the β-galactosidase plasmid (internal control). Luciferase activities are expressed as the percentage of the hNT-122 plasmid without NR2F2 and are the mean ± S.D. of four separate transfections after normalization to β-galactosidase expression.