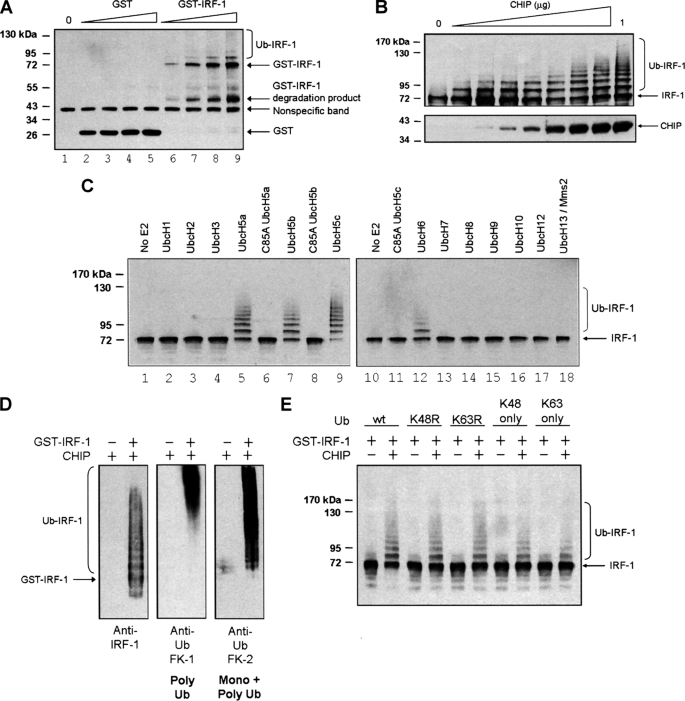
FIGURE 5.
CHIP-dependent ubiquitination of IRF-1 does not require Hsp70 and uses E2 enzymes of the UbcH5 and H6 families. A, an in vitro ubiquitination assay was assembled with purified E1, E2, His-CHIP, ubiquitin, and a titration (0, 25, 50, 75, and 100 ng) of GST-IRF-1 (or GST alone) in the presence of ATP. Ubiquitinated protein was analyzed by SDS-PAGE/immunoblot using anti-GST mAb. B, ubiquitination assays were assembled as above using a fixed amount of GST-IRF-1 (40 ng) and a titration of His-CHIP (0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 250, 500, 750, and 1000 ng). Immunoblots show total CHIP (bottom) and ubiquitinated IRF-1 (top) detected using anti-CHIP mAb and anti-IRF-1 mAb. C, ubiquitination assays were assembled as in A, using a constant amount of GST-IRF-1 and various E2 enzymes as indicated. Ubiquitinated protein was analyzed by SDS-PAGE/immunoblot, using anti-IRF-1 mAb. D, a ubiquitination assay was assembled as above with UbcH5a as E2, and total GST-IRF-1 was purified from the reaction mix using glutathione-Sepharose. Purified GST-IRF-1 was analyzed by SDS-PAGE/immunoblot using anti-IRF-1 mAb and anti-ubiquitin FK1 and FK2 antibodies. E, ubiquitination assays were assembled as above using WT ubiquitin and various ubiquitin mutants. Immunoblots were probed with anti-IRF-1 mAb.