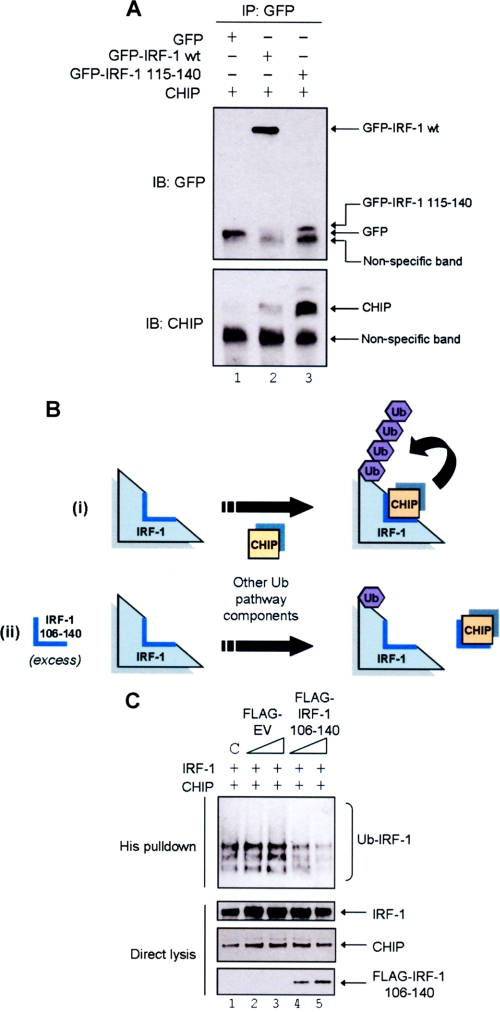
FIGURE 6.
IRF-1 aa 106–140 can act in trans to inhibit CHIP-dependent ubiquitination of full-length IRF-1. A, A375 cells were co-transfected with GFP alone, GFP-IRF-1 WT or GFP-IRF-1(115–140), and pcDNA3-CHIP. GFP conjugates were immunoprecipitated using anti-GFP pAb (IP) and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/immunoblot (IB) using anti-GFP mAb and anti-CHIP mAb. Results are representative of two separate experiments. B, model showing the requirement of aa 106–140 for IRF-1 ubiquitination. i, CHIP directly binds to IRF-1 aa 106–140 and ubiquitinates IRF-1. ii, the addition of IRF-1 106–140 in trans would compete with full-length IRF-1 for CHIP binding, resulting in a decreased ubiquitination of the full-length protein. C, H1299 cells were transfected with pcDNA3-IRF-1 WT (0.5 μg), His-ubiquitin (0.5 μg), pcDNA3-CHIP (2 μg), and a titration of FLAG-empty vector (EV) or FLAG-IRF-1(106–140) (1 or 2 μg); DNA was normalized using pcDNA3 empty vector, and C represents a control sample that was transfected with pcDNA3-EV but no FLAG constructs. Post-transfection (20 h) cells were treated with MG132 (50 μm) for 4 h. His-ubiquitinated protein was isolated and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/immunoblot developed using anti-IRF-1, anti-CHIP, and anti-FLAG mAbs.