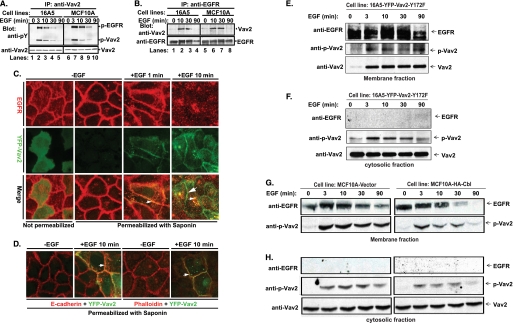
FIGURE 3.
EGF-induced phosphorylation of Vav2, association with EGFR, translocation of phospho-Vav2 to the cell membrane, and co-localization of Vav2 with EGFR, E-cadherin, or F-actin at cell-cell junctions. A, growth factor-starved 16A5 (lanes 1–5) or MCF10A (lanes 6–10) cells were stimulated with EGF (100 ng/ml). The whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Vav2 Abs and immunoblotted with anti-phosphotyrosine (pY) Abs and anti-Vav2 Abs or (B) IP with anti-EGFR Abs (clone 528) and immunoblot for Vav2 and EGFR. C, MCF10A cells with stable expression of YFP-Vav2 WT (green) were growth factor-starved and stimulated with EGF (100 ng/ml). The cells were either fixed directly (1st image from left) or permeabilized with saponin/PBS (10 μg/ml, 2nd to 4th images) for 10 min before fixation and then immunostained for EGFR (red). The yellow color indicates co-localization of YFP-Vav2 with EGFR (small arrowheads); the green color indicates cell junction-localized Vav2 (large arrowhead). D, cells were permeabilized as above and immunostained for E-cadherin (red, 1st and 2nd images from left) or F-actin (red, 3rd and 4th images). The yellow color indicates the co-localization of YFP-Vav2 with E-cadherin or F-actin (small arrowheads). E–H, growth factor-starved 16A5-YFP-Vav2–172F cells (E and F) or vector-expressing versus WT Cbl-overexpressing MCF10A cells (G and H) were stimulated with EGF (100 ng/ml) for the indicated time points. Whole cell lysates were subjected to subcellular fractionation. Membrane (E and G) and cytosolic (F and H) fractions were immunoblotted for EGFR, phospho-Vav2, and Vav2.