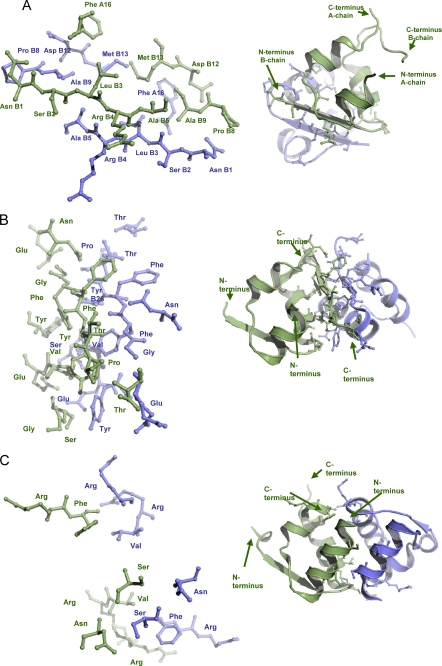
FIGURE 2.
The insulin dimers. A, shown is dimerization of DILP5 with dimerization site consisting of PheA16, Asn B1, SerB2, LueB3, ArgB4, AlaB5, ProB8, AlaB9, AspB12, and MetB13. B, shown is dimerization of human insulin with dimerization site consisting of AsnA21, GlyB8, SerB9, ValB12, GluB13, TyrB16, GluB21, GlyB23, PheB24, PheB25, TyrB26, ThrB27, ProB28, and ThrB30. C, shown is dimerization of human relaxin with the dimerization site consisting of SerA4, AsnA8, ArgA22, PheA23, ArgB13, ValB16, and Arg B17. The two monomers are colored in green and blue. The dimerization site in all three cases consists of residues involved in contacts less than 3.5 Å between monomers (shown as sticks).