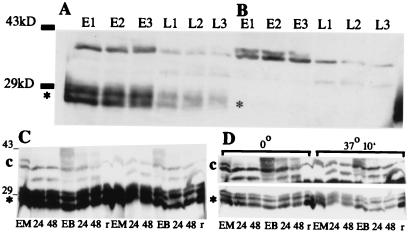
Figure 10.
Western blot analyses using antiserum against purified TRM1. Proteolysis in maize leaf extracts of TRM1 produced in E. coli and of endogenous immunoreactive material. (A) Purified TRM1(*) produced in E. coli was added to extracts of frozen ground leaves and extracted as described in Materials and Methods: etiolated leaf extract (E), extract of leaves from seedlings illuminated for 48 h (L). Samples were centrifuged and an aliquot was frozen immediately (E1, L1). A second aliquot was kept on ice for 30 min, then frozen (E2, L2). A third aliquot was kept on ice for 30 min, then at room temperature for 10 min and then frozen (E3, L3). (B) As above but no exogenous TRM1 was added. Bars to the left of the Western blot indicate the relative positions of ovalbumin (43 kDa) and carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa). (C and D) Proteolysis of cellular and E. coli-produced TRM1 in MC and BSC extracts. One microgram of TRM1 produced in E. coli was added to each of two MC and BSC extracts. Each extract contained 100 μg of cell protein. One MC and one BSC aliquot was kept on ice for 10 min, the other set was incubated at 37o for 10 min. (A) A single exposure of the Western blot with the relative amounts and positions of cellular TRM1 or (*) purified TRM1 produced by E. coli. (B) Two different exposures of the same Western blot to help clarify the differences in breakdown rates in the different samples. Extracts were loaded in the following order (first the samples kept at 0o, then those at 37o, as shown on B): MC from etiolated seedlings (EM), MC from seedlings illuminated for 24 h (labeled 24), and illuminated for 48 h (labeled 48), BSC from etiolated seedlings (EB); BSC from seedlings illuminated for 24 h (labeled 24), and illuminated for 48 h (labeled 48), and purified E. coli produced TRM1 without cell extract added (r). The numbers to the left of the blot show the relative positions of ovalbumin (43 kDa) and carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa).