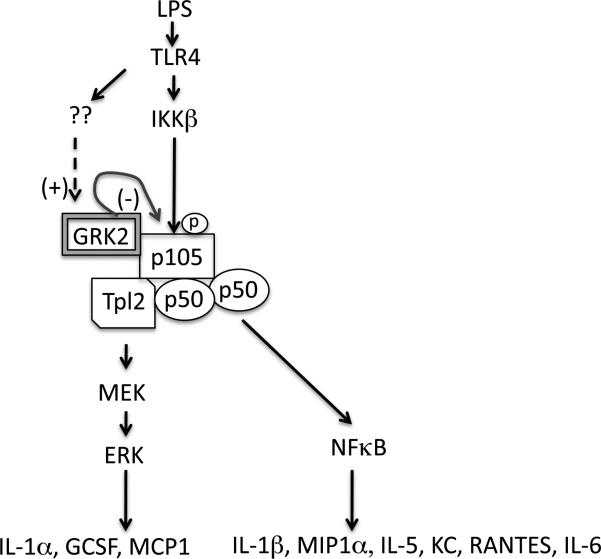
Figure 9. Proposed model of GRK2 regulation of TLR4-induced inflammatory response.
TLR4 activates ERK pathway via IKKβ-mediated phosphorylation of p105. Based on the results presented here, we propose that GRK2 negatively regulates IKKβ-induced p105 phosphorylation and therefore the ERK pathway. Because p105 phosphorylation is also essential for p50 mediated NFκB activation, negative regulation of p105 by GRK2 also modulates a subset of cytokines that are regulated by this pathway. Note that there are two exceptions: 1. Because MCP-1 was inhibited by ERK inhibitor but not by the IKKβ inhibitor, it is possible that MCP-1 is being regulated by GRK2 in an ERK-dependent but p105-independent mechanism. 2. Also, because MIP1α was modestly inhibited by PD98059, it is possible that a small component of the ERK pathway may also regulate MIP1α. Previous studies in primary macrophages and neutrophils have demonstrated that TLR4 activation increases the expression of GRK2 significantly and thus GRK2 might act as a negative feedback regulator for TLR4 signaling.