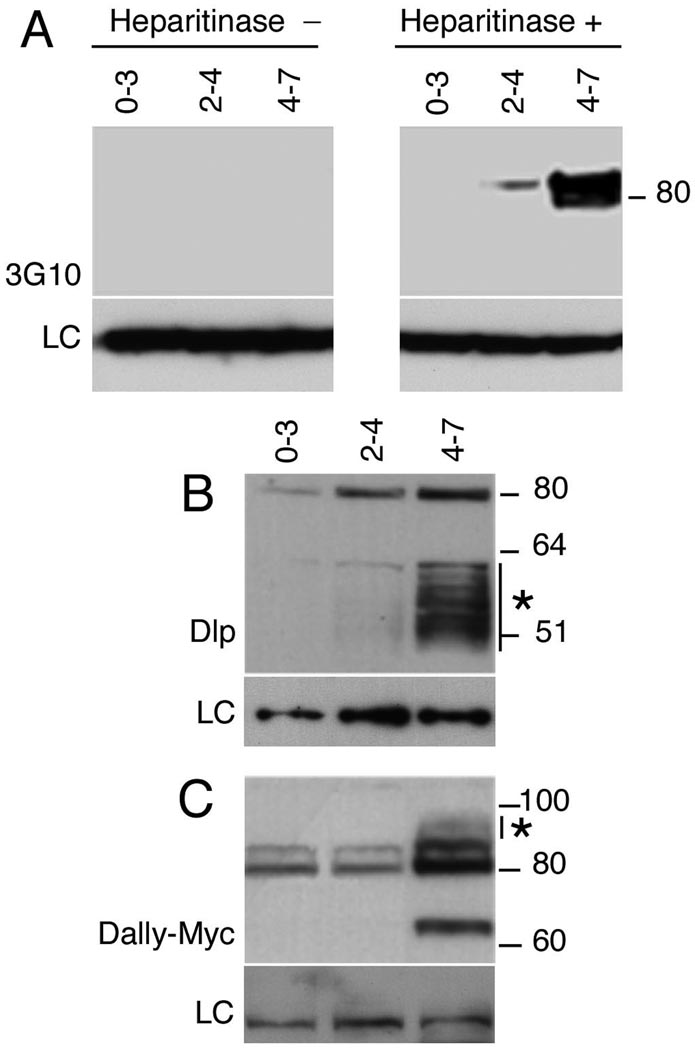
Figure 2. HSPG GAG chain synthesis is temporally regulated.
(A) Western blots of staged embryonic extracts probed with 3G10 antisera against GAG chain stub epitopes generated by heparitinase III digestion. GAG-modified core proteins are undetectable in 0–3 hour embryo extracts but are seen in 2–4 and 4–7 hour samples. No signal was detected in the absence of heparitinase. LC denotes loading control (B) Staged embryonic extracts were probed to with anti-Dlp to detect Dlp and (C) anti-Myc to detect Dally. matTub>Gal4 was used to drive UAS-Dlp or UAS-Dally expression maternally and embryonic extracts from the indicated stages resolved on reducing gels. Dlp was detected as a sharp band at 80 kDa corresponding to full-length protein and a heterogeneous band between 50 and 60 kDa that represents a GAG-modified cleavage product. Low levels of full-length Dlp are seen at 0–3 hours, but GAG modifications are essentially undetectable until 2–4 hour and are dramatically upregulated in 4–7 hour embryos. (C) Full-length epitope-tagged Dally is visible as an ~80 kDa doublet in 0–3 and 2–4 hour extracts. Significant levels of GAG modification are first apparent in 4–7 hour extracts as decreased mobility of the full-length protein (*). The ~65 kDa band is likely to result from processing by protein convertases, similar to vertebrate glypicans.